Connecting monitors to PCs has become a staple in both work and gaming environments. Whether you’re setting up a high-performance monitor for gaming or configuring a dual monitor setup for productivity, understanding the nuances of monitor connections is key. This article tackles the essentials of connecting various types of monitors, from HDMI-enabled displays to VGA monitors, ensuring you get the most out of your desktops and laptops.
Key Takeaways_
- Connecting a monitor to your PC is generally straightforward and requires no expertise.
- Adapters are widely and easily available for connecting nearly any combination of port types if needed.
- Not all port types support both video and audio.
Connecting Your Monitor to a PC

STEP 1 Connect the Video Cable
- Make sure your monitor is plugged into power and with the computer powered down.
- Determine the types of video connectors available on your PC and monitor, such as HDMI, VGA, DVI, and USB-C.
- We have a short breakdown of each connection further down on the page.
- Connect the appropriate video cable (HDMI, VGA, DVI) to your PC’s video output port.
- Secure the other end of the video cable to your monitor.
- For USB-C connections, ensure a firm connection to the USB-C port.
- Power on your computer and wait a few seconds- a Windows or Apple logo should appear if you’ve connected everything correctly.
STEP 2 Turn on Devices
- Power on your computer and wait a few seconds- a Windows or Apple logo should appear if you’ve connected everything correctly.
STEP 3 Configuring Display Settings
- Navigate to the display settings on your PC to adjust display options.
- After your computer boots up, check display preferences to make sure your settings are correct and that you’re getting the screen resolution, refresh rate, and aspect ratio intended.
- In Windows, go to Settings>System>Display and check the display resolution and display orientation.
- In macOS, go to System Settings>Display and check display resolution and picture orientation.
- See your operating system’s advanced display settings if anything needs tweaking.
Essential Equipment and Preparations
Before diving into the connection process, it’s crucial to identify the necessary equipment. Most modern monitors and desktops support HDMI and DisplayPort at a minimum, offering enhanced video and audio quality.
For older models, VGA cables might be more appropriate. Additionally, for devices like an HP monitor with Mini DisplayPort or a USB-C port, you’ll need a compatible video cable or an adapter, such as a USB-C to HDMI adapter.
STAT: Micro HDMI cables combine video and audio into an interface that is small enough to connect to tablets, smartphones, and other mobile devices. They are 50% smaller than the standard HDMI cables. (source)
Ensure you have the correct cable and power cables ready, and check the video output options on your PC.
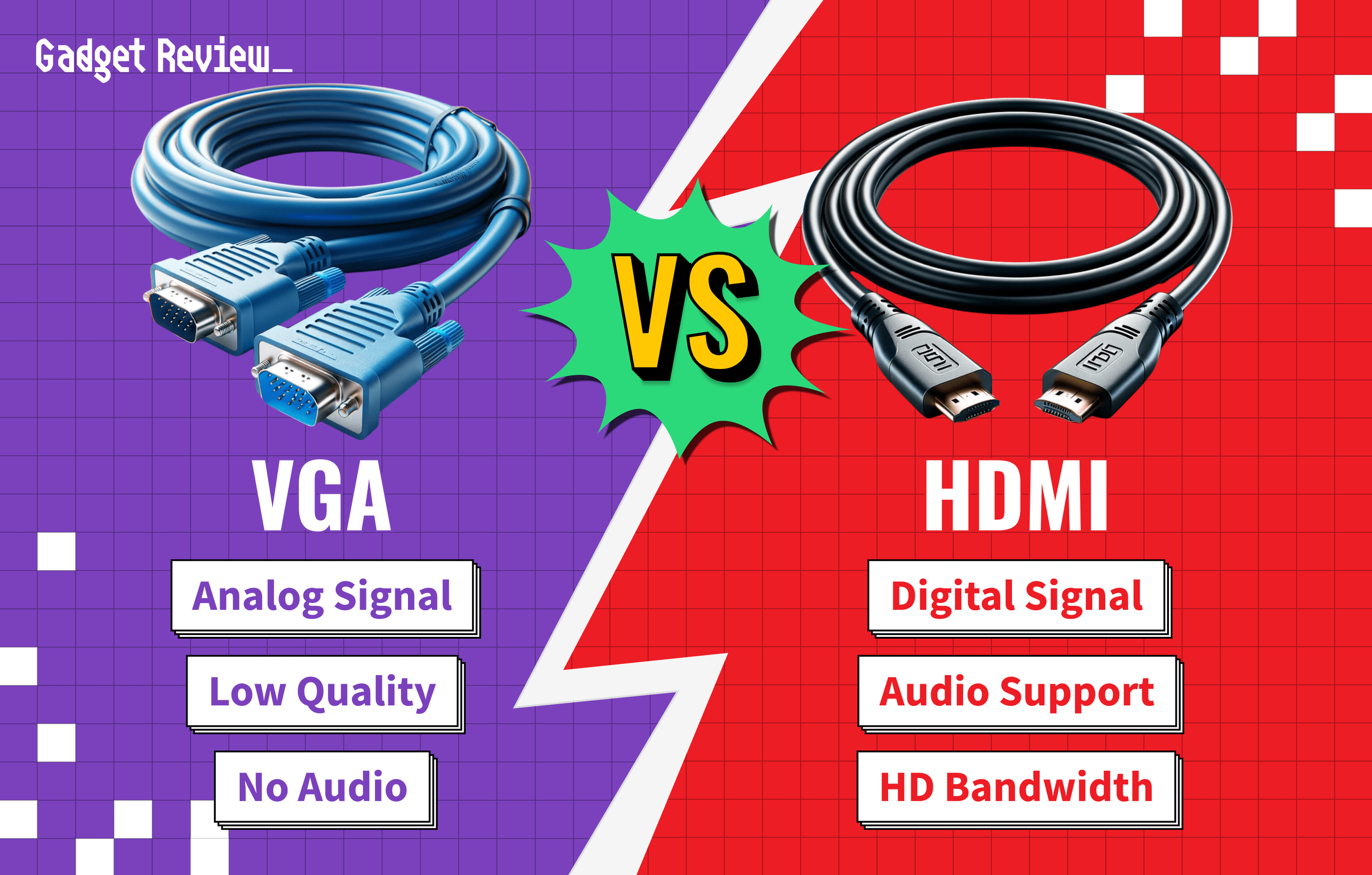
HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface)

A widely used interface for transmitting both video and audio signals. HDMI is known for its ability to deliver high-definition content, making it a popular choice for modern displays and multimedia devices. HDMI cables also make it easy to use a TV as a computer monitor.
- Pros: Supports high-definition video and audio, widely used, compatible with various devices. Offers lossless transmission and sharp text display.
- Cons: Limited cable length, potential compatibility issues with different HDMI versions.
DisplayPort

Designed to transmit high-definition video and audio signals. DisplayPort is often used in computer monitors and is known for its ability to support higher resolutions and refresh rates compared to HDMI. It’s also capable of connecting multiple screens over a single cable.
- Pros: High video resolution and refresh rate support, ideal for gaming and professional displays. Can connect multiple screens over a single cable.
- Cons: Not as widely adopted as HDMI, can be more expensive.
USB-C

Versatile connection type that can carry data, video, and power over a single cable and is increasingly used in modern laptops and monitors for its ability to support high-resolution displays and its compatibility with various protocols.
- Pros: Versatile, can carry data, video, and power over a single cable. Supports high-resolution displays.
- Cons: Not all USB-C cables support video transmission and require newer devices.
warning
Thunderbolt and USB-C ports look identical and have similar functionality, but they are different, with Thunderbolt having a higher transfer rate of 40Gbps compared to 20Gbps for USB-C.
Thunderbolt (especially Thunderbolt 3 and 4)

A high-speed interface that combines data, video, and power in a single connection, similar to USB-C. Thunderbolt, especially in its latest versions (3 and 4), offers high bandwidth and is capable of daisy-chaining multiple devices, making it ideal for high-performance applications.
- Pros: High data transfer rates, supports video, data, and power, and can daisy chain multiple devices.
- Cons: More expensive, requires compatible devices and cables.
DVI (Digital Visual Interface)
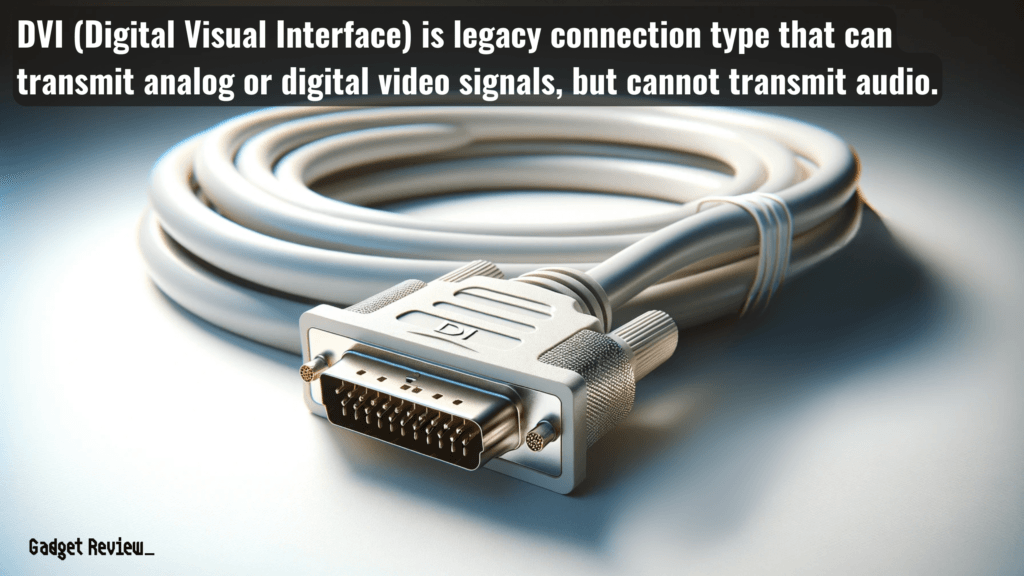
It is primarily used for connecting a video source to an external display device and supports both digital and analog signals, but it is more limited in bandwidth compared to newer offerings, like HDMI and DisplayPort. It’s commonly found in older computer systems.
- Pros: Good for older systems, supports digital and analog video signals.
- Cons: Does not carry audio signal, limited to lower resolutions compared to HDMI and DisplayPort.
VGA (Video Graphics Array)

An older standard that transmits analog video signals. VGA ports are typically used for lower-resolution legacy monitors and are less common in modern devices due to their limitations in video quality and lack of audio support.
- Pros: Common in older equipment, useful for compatibility with legacy systems.
- Cons: Analog only, lower image quality, does not support high resolutions or audio.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
- If your monitor doesn’t display an image, check the connections and ensure the correct video source is selected.
- For issues like poor image quality or no signal, try a different video cable or check for damaged ports.
- If using dual monitors, ensure both are correctly detected in your PC’s display settings. For extended desktop issues, adjust the display options from the drop-down menu in the display settings.
- Additionally, for a dual monitor setup, you can arrange the monitors in the display settings by dragging the monitor icons to match your physical setup. Adjust the primary display and secondary displays as needed.
- If you want to save space with a dual monitor setup, you can learn how to mount your monitors.
- For gaming or graphic-intensive tasks, ensure your HDMI or DisplayPort cables support the dynamic range and resolution of your monitors. Consider the layout of your monitors for ergonomic viewing.
- When connecting multiple monitors, such as in a dual monitor arrangement, it’s important to understand your PC’s capabilities and the maximum number of monitors it can support.
- Modern monitors like the LG monitor offer advanced features that may require specific cable types or connectors, like USB Type-C or a specific HDMI adapter.
In conclusion, connecting a monitor to your PC, whether it’s an external monitor for a laptop or additional monitors for a desktop, enhances your computing experience.
By understanding the types of video connectors, choosing the correct video cable, and optimizing your display settings, you can ensure a seamless and productive setup.