We all want to know what the best TVs are, but it’s hard to keep up with the ever-evolving world of specs and technology. So in this article, we match up the QLED TV vs LED and see where their strengths and weaknesses reside. Put simply, QLED TVs are LED TVs that have a layer of quantum dots between the LED backlight and the LCD display.
Differences Between QLED TVs and LED TVs
If you are shopping for a new TV, you have most likely come across the terms LED, QLED or OLED, and more. These can be confusing, but when comparing LED and QLED TVs, it’s essential to know that QLED is the latest LED display technology. Each display type deals with how the screen emits light and the complexity and structure of the light source.
insider tip
To get your LED TV to live longer, go to your settings and lower the brightness level.
LED and QLED Display Technologies Explained
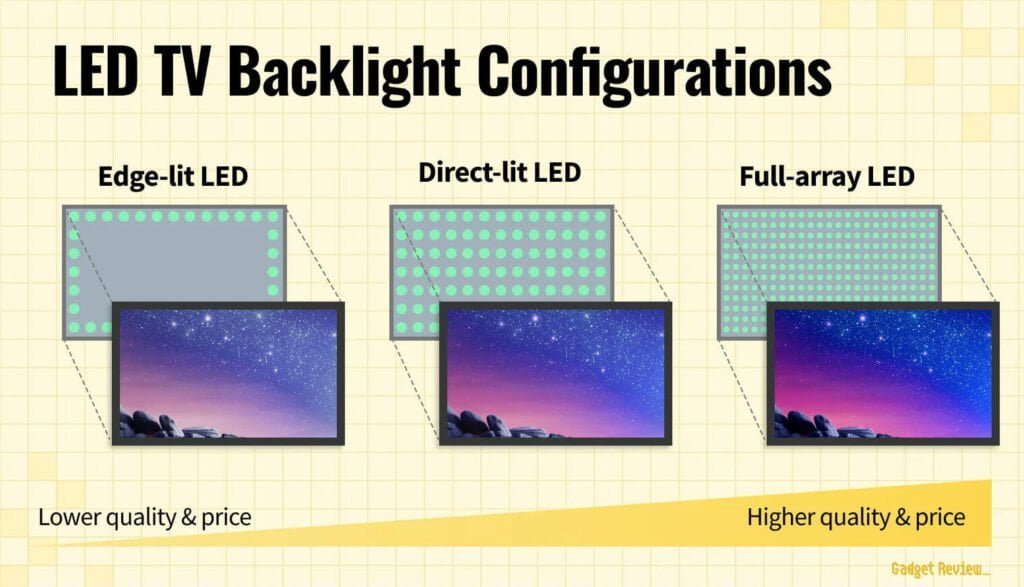
LED stands for “light-emitting diode.” This is a type of screen technology that uses an LCD panel alongside an LED backlight to emit color. There are three main configurations of LED displays:
- Edge-Lit LED – This is the most common configuration. LEDs are positioned on the edges of the screen, usually either along the top and bottom or on the left and right sides of the display. With the way the LEDs are positioned, there is less uniform brightness, but this is also the most affordable of the three configurations.
- Direct-Lit LED – With this configuration, the LEDs are positioned behind the LCD panel. This provides better control over local dimming and allows for more uniform brightness as well as improved contrast and black levels compared to edge-lit. These options may have slightly more thickness due to the LED placement.
- Full-Array LED – This configuration has the best backlight implementation of the three. These models are similar to direct-lit but use many more LEDs and are divided into zones, which provides more precise control over the local dimming zones and results in better contrast and black levels. As a general guide, the more dimming zones the TV has, the better the picture quality will be.
QLED stands for “quantum-dot light-emitting diode.” This display technology was developed by Samsung, however, other brands like TCL also sell QLED TVs. The quantum dot takes the LED backlight and filters it through an extra layer. The quantum dot layer enhances the performance of an LED TV by providing better color accuracy and brightness to deliver robust picture quality–think more vivid colors and more intense black levels.
As QLED is an evolution of LED, these models can have different backlighting configurations as well. Different manufacturers may have a specific name for their version of quantum dot technology for Sony and Samsung, respectively.
While quantum dot technology is the next step in LED models, there are still many other options for displays. We have a great comparison of LCD vs LED vs OLED that you can check out to see their pros and cons. We also have a comparison of just LED vs LCD TV if you don’t want OLED. Below, we’ll discuss some of the differences between LED vs QLED and help you understand which is best for your situation.
Picture Quality
It’s safe to say that of the two displays, QLED is a better option for getting vibrant and accurate colors and deeper blacks. The layer of tiny quantum particles produces rich colors, higher brightness levels, and better HDR (High Dynamic Range) performance than LED. In addition, it offers a wider color gamut than LED displays. Check out our Samsung 7 Series curved 65″ QLED review for a great QLED option.

LED TVs offer good picture quality, but the picture quality will greatly depend on the backlight configuration used. Full-array LED TVs can produce excellent picture quality but will not be able to match the brightness, black levels, or color gamut of QLED but are priced more budget-friendly.
Contrast Ratio
QLED TVs, especially the models equipped with local dimming, allow for a higher contrast ratio. This means you will see deeper blacks, as well as brighter highlights in HDR content.

LED TVs can struggle with backlighting, depending on the configuration. As such, they cannot replicate the deep blacks of QLED as the backlighting can have light bleed, whereas dark scenes can look more gray than black. While full-array local dimming can help, it won’t be as effective as QLED.
Viewing Angle
QLED TVs generally have good viewing angles. The image quality will diminish at extreme angles, though.
LED TVs have good viewing angles as well, but not as good as QLED, as the backlight can result in contrast or color shifts when you view the screen from off-center.
Energy Efficiency
LED TVs are great for conserving energy because they can achieve high brightness levels while staying relatively low on power consumption. This unique combo makes them great for any buyer looking to save on power.
QLED TVs are great for energy-conscious consumers as well, but it should be noted they may use more energy as they cause an additional layer compared to a regular LED TV. The screen size, brightness level, and usage will determine the TV’s energy efficiency.
Size and Variety
Both QLED and LED TVs are available in a wide range of sizes, from small to very large displays. Either TV can be a good option for various room sizes and viewing needs.
Price
The average price of a QLED TV has dropped in recent years, but the old phrase ‘reassuringly expensive’ still rings true. A QLED TV will run you more than the average LED TV, so if the price is a significant point of consideration, you may want to research LED options. Also, remember that the backlight configuration will affect the price of the TV as well. These will range from budget-friendly to high-end models but will usually be more affordable than QLED models.
Additionally, for perspective, an OLED TV is the most expensive on the market. And if that makes you wonder, “What is an OLED TV?” Be sure to understand what that display technology is as well before making a purchase. OLED is superior in terms of picture quality, color accuracy, and deeper blacks but will cost more than both of these other displays. So if you are out there looking, a QLED TV can be an excellent choice for a higher-end picture quality that doesn’t completely drain the bank account.
[convertkit form=7086165]