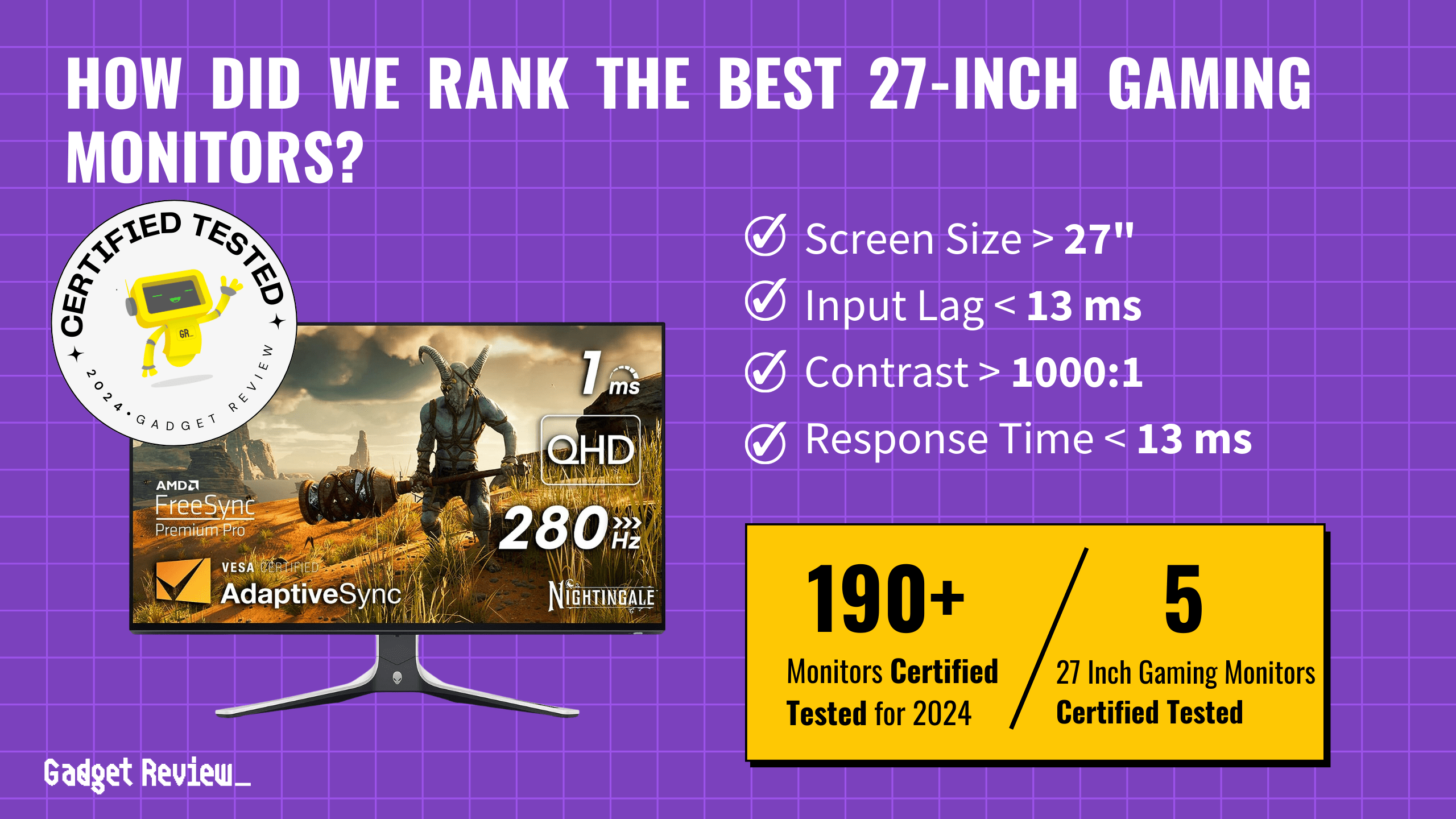
Video Graphics Array (VGA) has been a cornerstone in the world of computer graphics. Introduced by IBM in 1987, VGA revolutionized how computers displayed graphics on monitors. Below we will look at the intricacies of VGA, from its definition to its evolution, technical specifications, and current applications. We’ll explore how VGA, with its distinctive 15-pin connector and analog signals, set a standard in the early days of personal computing and how it compares to modern digital interfaces like HDMI and DP on today’s top computer monitors.
Key Takeaways_
- VGA connections were created in 1987 by IBM.
- VGA only supports video display and cannot transmit audio.
- VGA relies on analog signals and features limited display outputs.
What is a VGA Connector?
VGA, or Video Graphics Array, is a graphics standard for computer display systems. It was the first to offer color display capabilities on computers, a significant leap from the monochrome displays of the past.
VGA uses analog signals to transmit video data from the graphics card to the monitor, allowing for a range of resolutions and color depths.
Optimizing Your Monitor Setup
Discover the key differences and advantages of using a monitor vs a TV for your display needs. If you’re deciding between VGA and HDMI, knowing the pros and cons of each can help you make an informed choice. For gamers, it’s crucial to find the best aspect ratio for gaming and to understand how your monitor affects gaming performance. Additionally, if you’re setting up multiple devices, here’s a guide on how to connect a PS4 to a monitor and how to connect a monitor to a PC seamlessly.
The standard VGA connector, a 15-pin D-subminiature connector, became ubiquitous in the computing world and is found on a wide range of devices from monitors to projectors.
insider tip
Sometimes VGA is referred to as SVGA today, which is an extension of VGA not developed by IBM. It increased the maximum resolution and memory of VGA, allowing for a resolution of 800×600.
The port was specifically designed to support IBM’s PS/2 PC series. In particular, it was perfect for analog connections with the classic cathode ray tube (CRT) monitors.
The Evolution of VGA
Since its inception, VGA has undergone significant transformations.
Originally supporting a resolution of 640×480 pixels in 16 colors, VGA’s capabilities were quickly expanded.
STAT: VGA provides 640 x 480 resolution color display screens with a refresh rate of 60 Hz and 16 colors displayed at a time. If the resolution is lowered to 320 x 200, 256 colors are shown. (source)
Modes like Mode 13h allowed for 256-color displays, while extended modes pushed the boundaries of resolution and color depth.
VGA’s adaptability made it a lasting standard in an industry marked by rapid technological advancements.
Technical Specifications of VGA
VGA’s technical specifications are a testament to its enduring legacy. It supports a maximum resolution of 640×480 pixels with a refresh rate that minimizes screen flicker.
warning
When dealing with VGA connections and older monitors, it’s essential to be aware of potential compatibility issues. Also, be cautious when selecting video connections, as choosing between HDMI and DVI for gaming can significantly impact your gaming experience. If you’re wondering, “What is DVI?” It’s a type of video connection that can offer better performance for gaming compared to VGA.
VGA cables transmit analog video signals, which can suffer from signal degradation with low-quality cables or over long distances.
However, the use of coaxial wiring in VGA cables helps mitigate this issue. VGA ports are still found on many modern computers, offering compatibility with a wide range of display devices.
How to Set Up and Use VGA
Setting up a VGA connection is straightforward. Like other display connection cables, it involves connecting a VGA cable from the VGA port on the computer to the VGA monitor or projector.
STAT: The VGA interface includes no affordances for hot-swapping and the ability to connect or disconnect the output device during operation, although in practice, this can be done and usually does not cause damage to the hardware or other problems. The VESA DDC specification does, however, include a standard for hot-swapping. (source)
For devices without a VGA port, HDMI to VGA or DVI to VGA converters can be used. Ensuring the correct screen resolution and refresh rate settings on the computer enhances the display quality.
VGA vs. Modern Alternatives
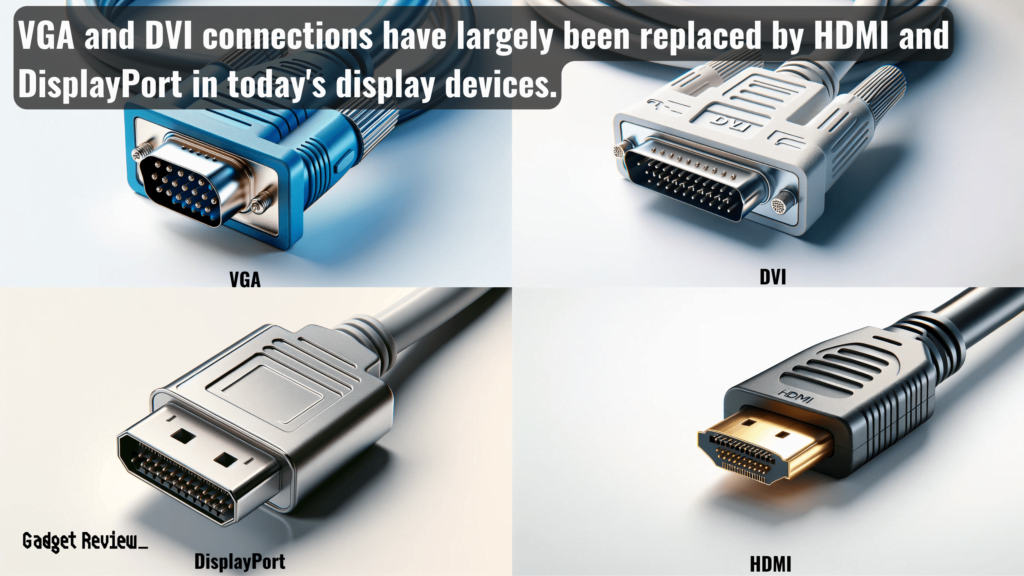
Comparing VGA to modern alternatives like HDMI, DVI, and DisplayPort highlights its limitations in today’s digital age.
VGA’s analog nature means it can’t match the higher resolutions and sound quality of digital interfaces like HDMI 2.1.
However, VGA’s simplicity and widespread adoption have ensured its continued use.
Enhancing Your Workspace
A well-organized workspace can greatly enhance your computing experience. Consider investing in the best monitor stand to improve ergonomics and reduce strain during long periods of use. Proper cable management is also crucial; explore the best cable management solutions to keep your setup tidy and safe. For those looking to add a bit of flair to their setup, the best RGB strips for PCs can provide aesthetic lighting without causing additional heat or power issues.
Despite the advent of those digital interfaces, VGA remains relevant in various applications thanks to compatibility with older hardware, making it a go-to option in legacy systems, especially in settings where high resolution is not paramount.
VGA cables and converters are widely used to connect modern computers to older monitors or projectors, demonstrating VGA’s enduring utility.
In contrast to VGA, modern display technologies like Thunderbolt monitors have emerged, which provide lightning-fast data transfer speeds and high-resolution video output, making them ideal for professional and creative work.
The Future of VGA
The future of VGA in our increasingly digital world is uncertain.
While it may not compete with the higher resolutions and digital video signals of modern interfaces, VGA’s simplicity and compatibility with a wide range of resolutions and devices ensure its continued presence in certain sectors.
insider tip
Even though VGA is no longer the preferred choice for display connections, these connections are still found on flatscreen televisions and monitors.
VGA has played a pivotal role in the development of computer graphics. From its standard 16-color mode to the more advanced 256-color mode, VGA set the foundation for future graphics standards.
Its legacy continues in various forms, from the VGA interface on older computers to VGA adapters used in modern devices. VGA’s story is one of adaptability and endurance in the exciting and fast-paced world of technology.