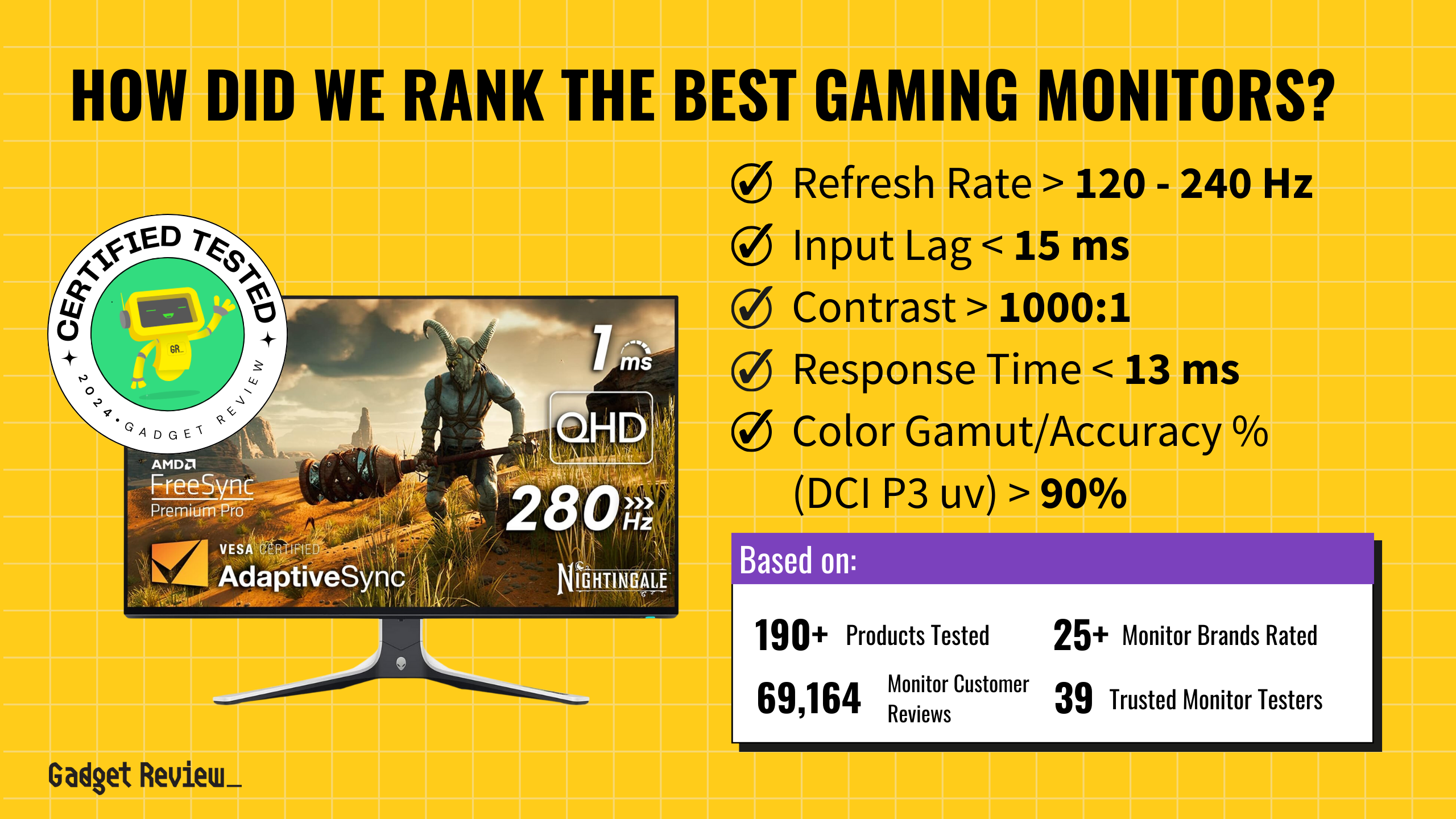
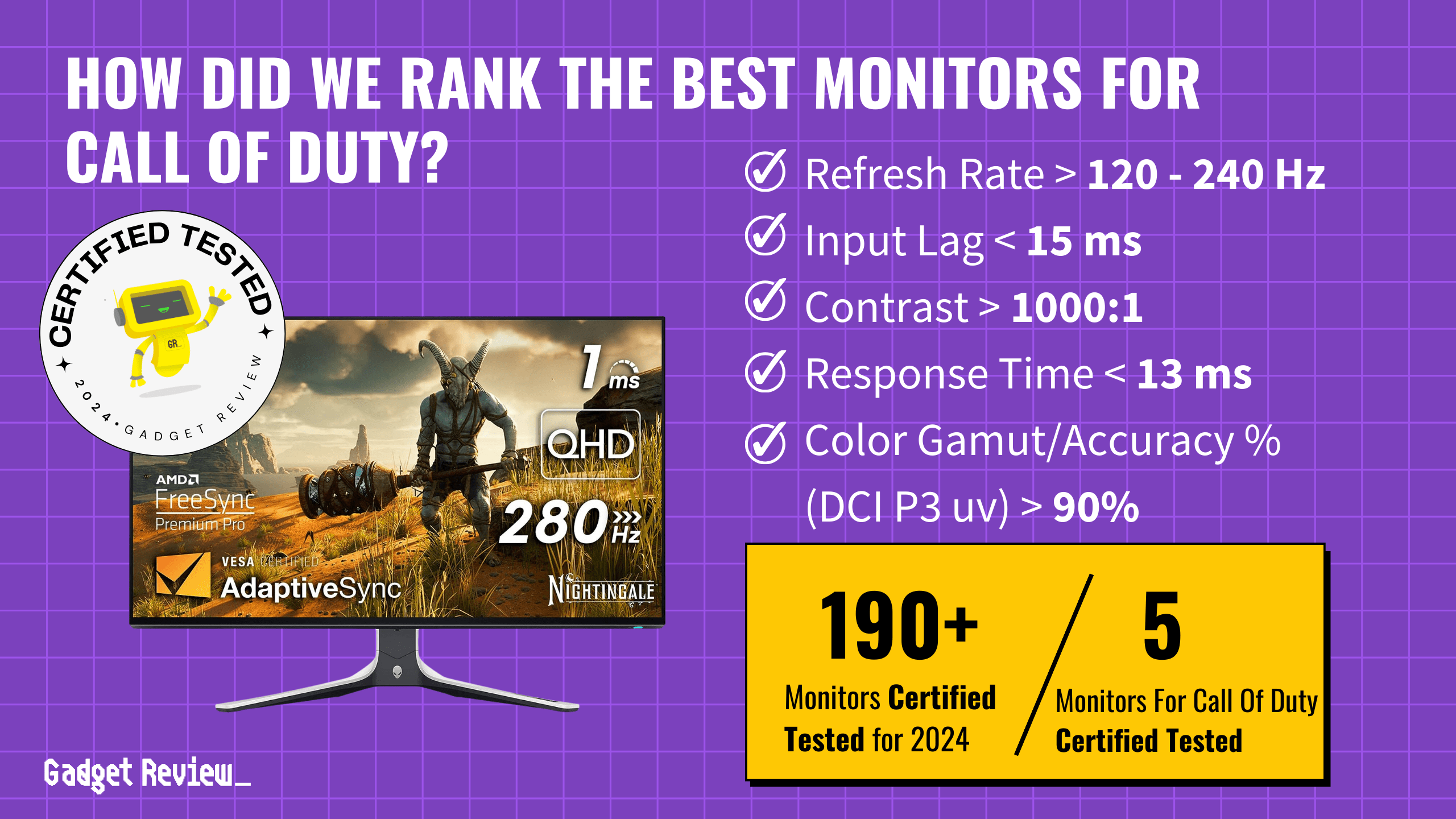
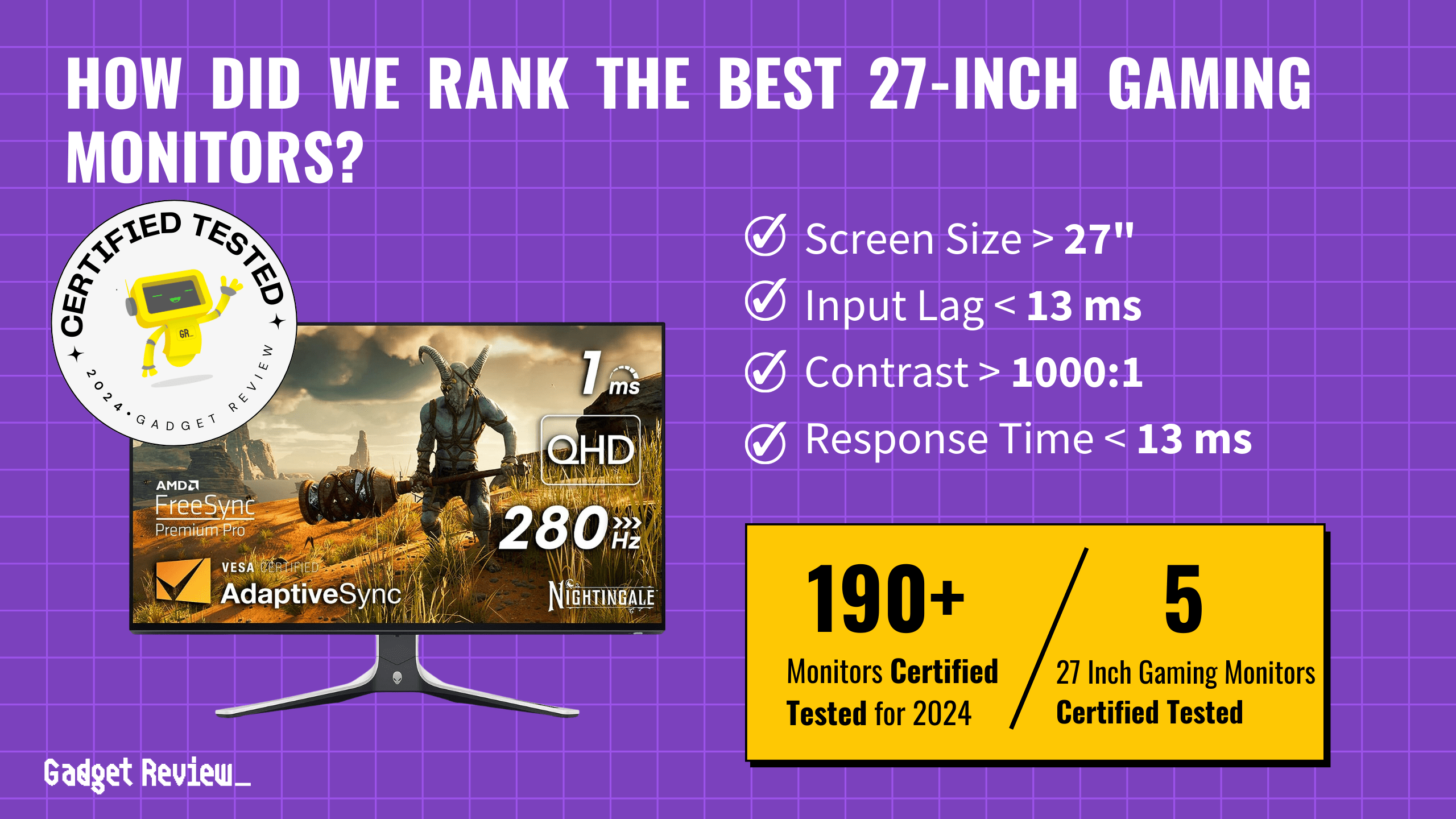
CRT monitors, once the standard in display technology, have a rich history. These monitors, known for their deep, curved screens, were ubiquitous in households and offices. They operate on the principle of cathode rays, where electrons emitted by an electron gun strike phosphor dots on the screen to create images. Despite the advent of flat-panel displays like LCD becoming the top computer monitors, CRTs hold a unique place in the evolution of display technologies.
Key Takeaways_
- CRT technology was first invented in 1897 in Germany.
- Between the 1990s to the 2000s, CRT monitors outsold flat-screen displays.
- Price drops in flat-screen displays led to the death of CRT monitors.
Younger individuals might not remember a time before flat-screen televisions or even LCD and LED monitors. But once upon a time, CRT monitors were big, heavy, and took up most of your desk.
Once a brand standard, they’ve now fallen out of favor as slim monitors that free up space and aren’t a pain to move are now the gold standard, which you can even hook up to your wall if you know how to mount a monitor.
But cathode-ray tubes or CRT monitors were a major stepping stone in technology for their time.
What is CRT?
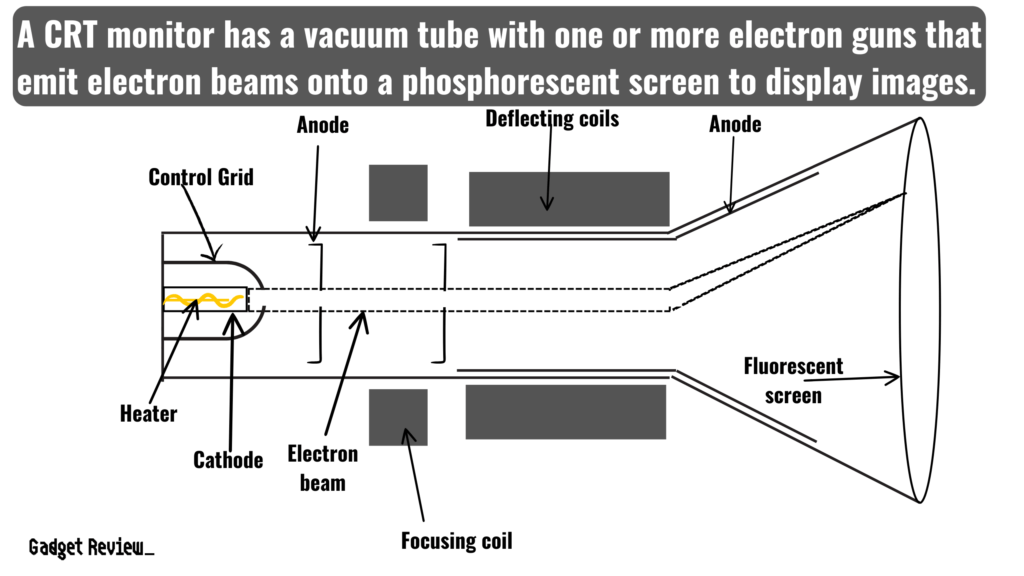
A Cathode-Ray Tube (CRT) monitor is a type of display device that uses a vacuum tube and electron guns to display images.
The heart of a CRT monitor is the cathode ray tube, where electrons flow from a heated cathode toward a phosphor-coated screen.
When these electrons, controlled by magnetic deflection, hit the screen, they illuminate the phosphors to create visible images.
Cathode Rays were discovered by German physicists Johann Hittorf and Julius Plücker in 1869 and further developed by others.
The “Braun tube,” invented in 1897 by German physicist Ferdinand Braun, would become the earliest use of CRT as a display device.
It wouldn’t be until 1926 when Kenjiro Takayanagi demonstrated a CRT TV receiver that could support images in a 40-line resolution. However, the first commercially available CRT television wouldn’t become available until 1934 in Germany by Telefunken.
How CRT Monitors Work
The operation of a CRT monitor involves a complex flow of electrons within a vacuum tube. The electrons emitted by the cathode are accelerated and focused into a beam by an electron gun.
This electron beam then passes through a deflection yoke, which directs the beam toward specific points on the phosphor-coated screen.
Understanding Monitor Types and Connections
Exploring the various types of monitors can help you select the best one for your needs. Exploring the distinctions between a monitor and a TV can offer insights into their unique features and use cases. Additionally, familiarizing yourself with what VGA is can help you navigate connections for older monitors.
That screen is divided into tiny red, green, and blue phosphor dots, and the intensity of the electron beam determines the brightness of each dot, combining to form the full spectrum of colors on the monitor screen.
In contrast, pixel density is important with modern displays, which refers to the concentration of pixels on a screen, measured in pixels per inch (PPI)—higher pixel density results in sharper and more detailed images, which is especially important for high-resolution monitors.
Advantages of CRT Monitors
CRT monitors offer several advantages over modern LCD displays.
- They are capable of displaying a wide range of resolutions and refresh rates without the need for scaling.
- CRTs are known for their color accuracy, deep blacks, and smooth rendering of motion, making them a preferred choice for applications like retro gaming.
- The analog nature of CRT technology also allows them to display an analog signal without the need for a converter, providing a more direct and responsive image display.
Challenges and Limitations
warning
Using a TV as a computer monitor may not be ideal due to pixel density and response time differences. Understanding these can help avoid issues. DVI connections can enhance monitor performance and compatibility. Monitoring CPU temperature while gaming is crucial, as overheating can affect functionality. Additionally, knowing how to set up dual monitors for gaming optimizes your setup and avoids common pitfalls.
Despite their advantages, CRT monitors have significant challenges.
- Their size and weight, due to the large glass tube, make them less practical than flat-screen displays.
- They consume more power and can emit a higher level of radiation.
- CRTs also pose environmental concerns; they are considered hazardous household waste due to the lead and other toxic substances in the glass and components.
- Disposal and recycling of CRTs are challenging, contributing to greater electronic waste issues.
The Evolution of CRT Monitors
CRT technology has evolved significantly since its inception.

Early CRT monitors in the 1970s were monochrome, displaying text in a single color, usually green.
Over time, color monitors emerged, using multiple electron guns, and by the end of that decade, color CRT computer monitors were widely available.
As time progressed, tech and electronics firms ranging from IBM to RCA and even Zenith all worked to upgrade CRTs by releasing innovations that made them more effective as computer companions.
warning
CRT Monitors are best known for their oversized design with large physical casings that are heavy.
The development of CRTs saw a shift from bulky, heavy glass tubes to more compact and efficient designs, though still much heavier than current flat-panel designs.
STAT: In the mid-1990s, some 160 million CRTs were made per year. (source)
Notable contributions to this evolution include the development of a practical color CRT and the introduction of flat-screen CRT monitors, which reduced the depth and weight of these devices.
CRT Monitors in the Modern Era
In the modern era, CRT monitors have seen somewhat of a resurgence in niche markets, particularly among retro gaming enthusiasts.
These monitors provide an authentic experience for playing classic games, which were originally designed for CRT display technologies.
insider tip
Some gaming purists who prefer to play older games prefer using CRT monitors because some older games were specifically designed for analog displays
The airline industry still uses CRT monitors in the cockpit, with both the Boeing 747-400 and Airbus A320 relying on the technology for aviation instruments.
However, finding and maintaining CRT monitors can be challenging, as production has largely ceased, and existing units are aging.
Maximizing Your Monitor’s Color Accuracy
For those who are particular about color accuracy, it’s essential to understand the differences between DCI-P3 vs sRGB to ensure the best color representation on your monitor. To achieve the best gaming experience, consider what brightness settings are optimal for your monitor. Enhancing your setup with the best RGB strips for your PC can also add a visually appealing touch to your workspace.
CRT communities often share resources and knowledge for repair and preservation, keeping the legacy of these monitors alive.
CRT monitors represent a significant chapter in the history of display technology. From the early experiments of Johann Wilhelm Hittorf to the sophisticated color monitors used in the late 20th century, CRTs have played a pivotal role in the development of electronic displays.
STAT: In 1934, the first CRT televisions were made available commercially in Germany by Telefunken. (source)
While modern LCD and flat-screen displays have largely replaced CRTs, their impact on gaming, television, and computing is undeniable.
As technology continues to advance, the CRT monitor remains a fascinating example of innovation and adaptation in the field of electronics.