There are a number of different types of high-quality computer monitors, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. These computer monitor types can be grouped into different categories. We will break down these different types: CRT, LCD, LED, and OLED to better help you choose the best monitor for your needs.
Key Takeaways_
- There are several different monitor types, such as CRT, LCD, LED, and OLED.
- LCD displays make up the lion’s share of the market, due to being made from inexpensive components.
- In addition to type, monitors come in a variety of shapes and sizes.
Types of Monitors
Generally speaking, there are four common types of computer monitors, though one is pretty much obsolete at this point. Consider learning about how monitors work in general while you’re learning about the different types of monitors.
Cathode Ray Tube Monitors
You may be asking yourself what is a CRT monitor? Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) monitors are the oldest display type.

These CRT monitors date back to the first computer screen, and the design is based on what was typically found in early television sets.
insider tip
Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) monitors are the oldest display type.
This design uses cathode fluorescent technology and cold cathode backlights.
warning
Due to the nature of the design, CRT displays can be extremely bulky and heavy and, as such, have fallen out of fashion in recent years.
They are still the preferred choice for playing vintage video games and using older software applications. But, with all the newer monitors now available, there aren’t many functions and uses for these computer monitors today.
LCD Monitors
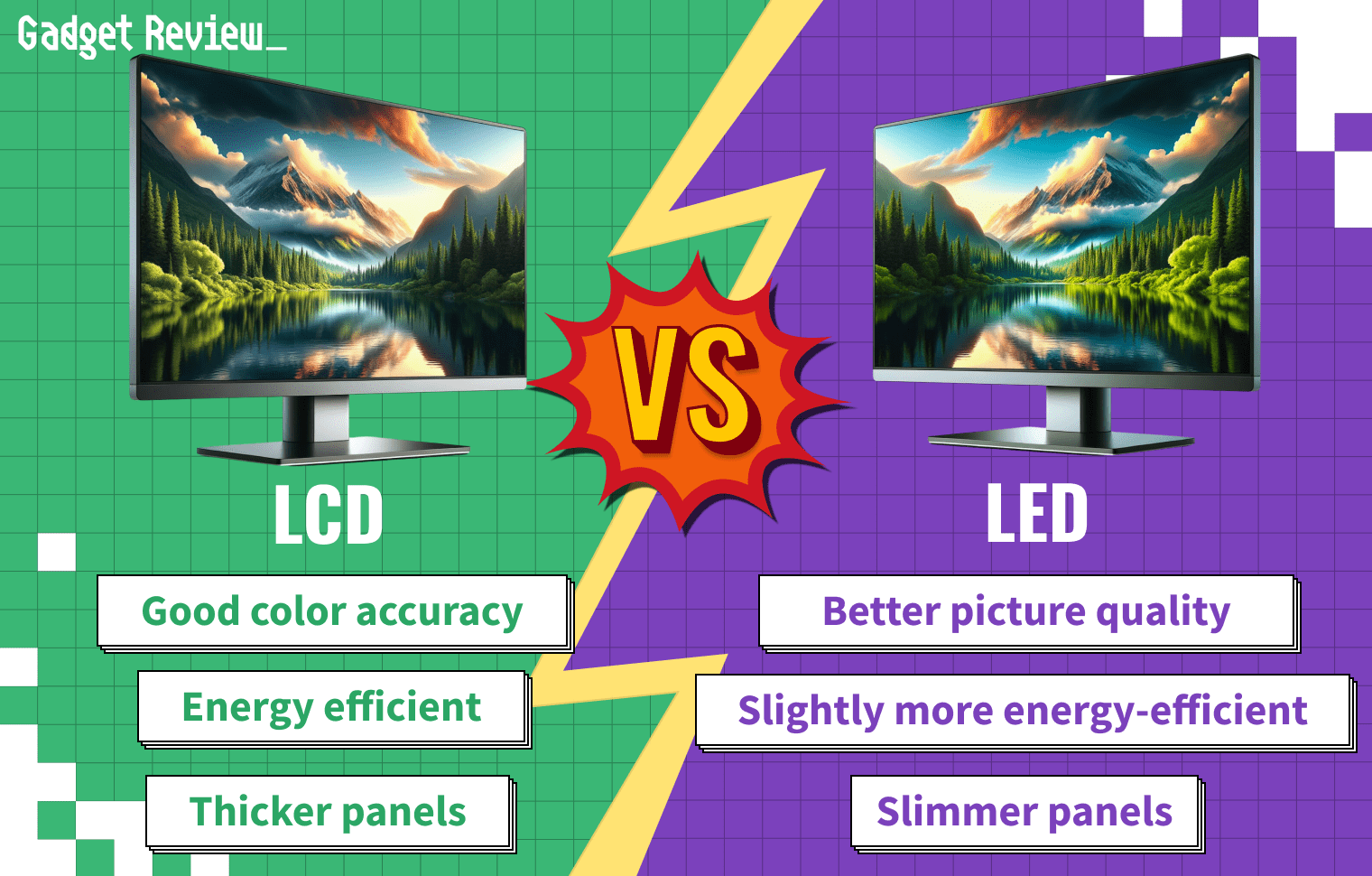
Liquid Crystal Displays (LCD) make up the lion’s share of modern computer screens that are available for purchase.
LCD technology has evolved significantly over the years, offering improved image quality and accurate color reproduction, which is especially important for content creators and professional monitors.
insider tip
These displays have gotten extremely cheap to produce and generally offer an optimized experience for most basic computing tasks, including gaming and video editing.
LCD screens are known for their wide viewing angles and 60Hz refresh rate, which is standard but can go much higher in specialized models.
warning
LCD monitors can vary wildly when it comes to resolution and other metrics, so do your research before making a purchase.
There are a number of different sub-categories that fall underneath the LCD umbrella, each of which is designated by its panel type.
LED Monitors
Light-emitting diode (LED) displays feature a technology that works similarly to what is found inside LCD monitors.
The main difference? A traditional LCD monitor uses fluorescent backlights, and an LED monitor uses light-emitting diodes for backlights.
LED monitors are generally considered to offer a better overall experience, with higher resolutions and brighter colors, but they can be on the expensive side.
OLED Monitors
Organic light-emitting diode (OLED) monitors are the latest and greatest innovation in display technology.
This design was originally used to manufacture high-end televisions with fantastic resolutions, 4K and 8K, but has since gone on to be used with computer monitors.
OLED monitors offer ultra-fast pixel response times, incredibly high resolutions, and superb contrast ratios.
However, OLED monitors are more expensive due to the nature of their internal components. The prices of OLED displays should drop significantly in the years to come as components become cheaper to manufacture.
Ultra-Wide & Curved Monitors
If you regularly watch Hollywood movies on your computer display, then you may want to go with an ultrawide monitor.

These monitors have wider aspect ratios than what is found with traditional screens. Average monitors clock in with a 16:9 aspect ratio, while ultrawide features a 21:9 aspect ratio.
These offer a much broader screen size and are usually curved monitors that provide an immersive experience by increasing screen space and offering curved screens that mimic the natural curvature of the human eye.
The end result is an extremely enjoyable viewing experience.
How Monitors Are Commonly Used Today
The way you want to utilize the monitor should be taken into account when choosing one. Specific characteristics, such as panel type, resolution, and refresh rates, are needed for various applications. A summary of the most typical monitor use scenarios is provided here.
| Use Case | Key Monitor Features |
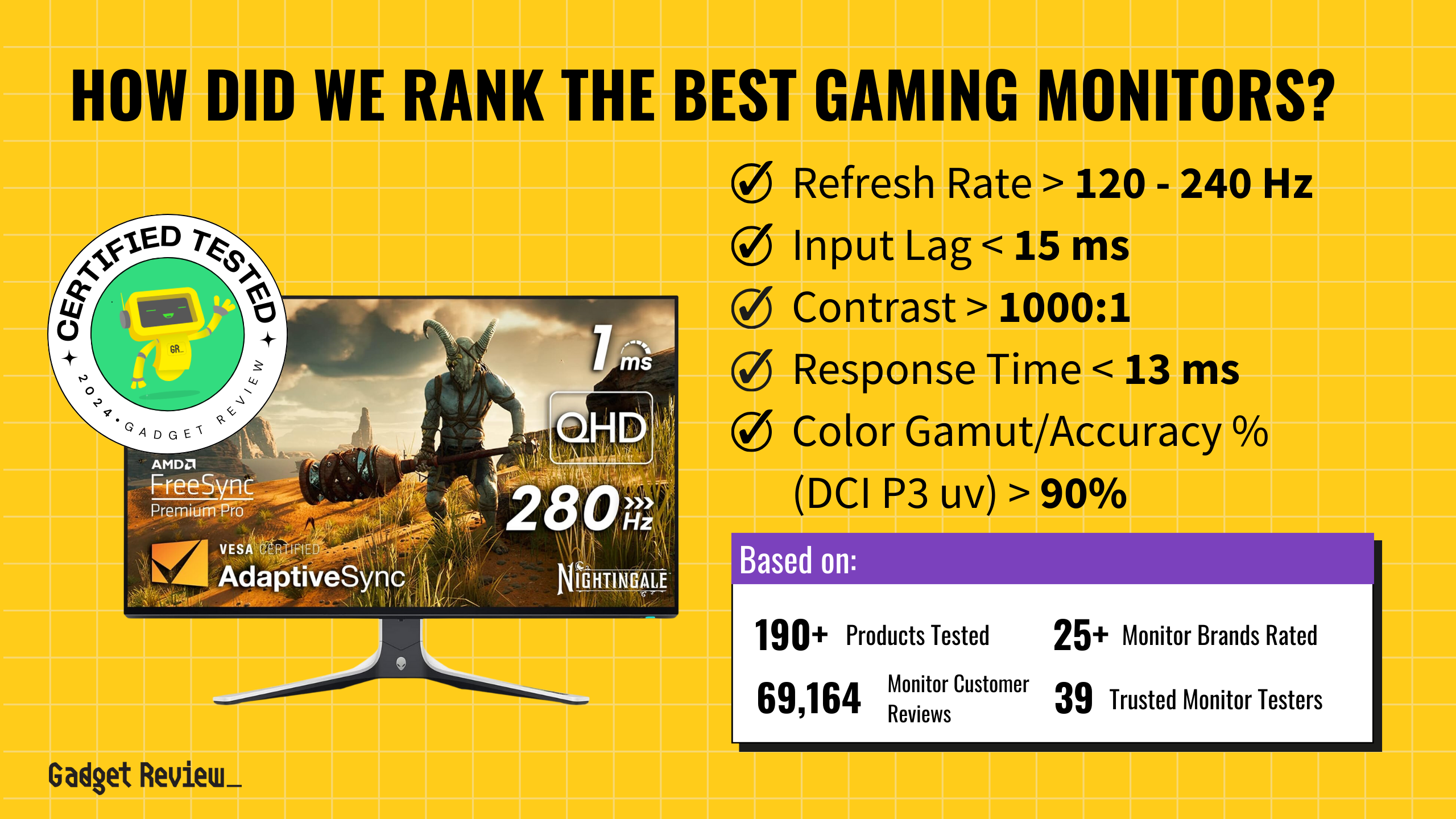
| Gaming | High refresh rate (120Hz–240Hz), low input lag, fast response times (1ms), G-Sync/FreeSync |
| Content Creation | High color accuracy (AdobeRGB, sRGB), wide viewing angles, 4K+ resolution, IPS or OLED panels |
| Office Work | Eye-care technology, adjustable stands, Full HD or QHD resolution, flicker-free panels |
| Media Consumption | Large screen size, OLED or VA panels for deep contrast, 4K UHD resolution, built-in speakers |
| Programming | Vertical monitor support, anti-glare coating, dual-monitor compatibility, sharp text rendering |
Pro Tip: Always match monitor specs with your primary use — not all users benefit from high-end specs like gamers or designers do.
Monitor Panel Types
There are a number of different types of panel technology, including In-Plane Switching (IPS), Twisted Nematic (TN), Vertical Alignment (VA), and Organic light-emitting diode (OLED).
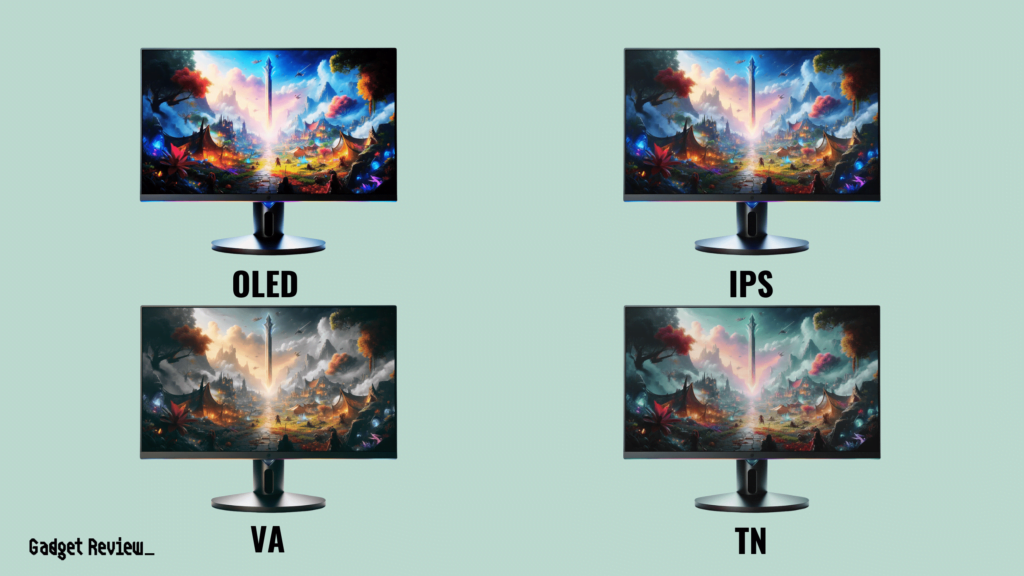

Each of these panel types offers its own advantages and disadvantages.
IPS Monitors
- IPS panels are known for their wide horizontal viewing angles and accurate color representation, thanks to the widest color gamut and superior color fidelity, making them ideal for professional content creation.
- They are, however, known to have “IPS glow,” where the edges of the screen glow when showing dark content, impacting the immersiveness in dark environments.
TN Monitors
- TN panels offer faster response times, often the fastest response times on the market. Their quick response times make them less likely to experience motion blur, making them ideal for gamers, especially in fast-paced competitive gaming.
- TN monitors do not have great viewing angles, meaning when you view the monitor off-center, the image will have a significant color shift or image fade.
VA Monitors
- VA panels are known for their deep blacks, which provide a more immersive experience, especially for movie enthusiasts.
- They can experience burn-in, a condition where pixels lose brightness over time and leave image silhouettes on the screen.
Of the three LCD panel technologies above, IPS panels are generally known for offering the best color accuracy and highest resolution.
Comparison Table: Monitor Panel Types at a Glance
Understanding panel technologies is crucial when choosing a display. Here’s a side-by-side comparison of the most popular monitor panel types:
| Panel Type | Best For | Pros | Cons |
| IPS (In-Plane Switching) | Content creators, professionals | Exceptional color accuracy, wide viewing angles | Slight backlight glow (“IPS glow”), slower response time |
| TN (Twisted Nematic) | Competitive gaming | Fastest response time, low input lag | Poor color reproduction and narrow angles |
| VA (Vertical Alignment) | Entertainment, general use | Deep blacks, strong contrast | Potential ghosting, slower refresh response |
| OLED (Organic LED) | Premium users, designers | Perfect blacks, ultra-fast pixel response, no backlight needed | High price tag, risk of image retention (burn-in) |
Quick Tip: IPS is ideal for color work, TN for speed, VA for rich contrast, and OLED for the best all-around visual experience.
Emerging Monitor Technologies to Watch
Monitor innovation is rapidly evolving. Here are the latest cutting-edge technologies shaping the future of displays:
- Mini-LED Displays
- Thousands of tiny LEDs for better brightness control and contrast
- Enhanced HDR performance
- Great for high-end gaming and creative professionals
- QD-OLED (Quantum Dot OLED)
- Combines OLED’s true blacks with quantum dot vibrancy
- Brighter visuals, better color accuracy
- A perfect hybrid for both gamers and creators
- Touchscreen Monitors
- Interactive displays for hybrid workspaces, education, and kiosks
- Popular in business settings and creative industries
- Portable USB-C Monitors
- Lightweight, plug-and-play convenience via USB-C
- Ideal for digital nomads, freelancers, and multi-screen professionals
Why It Matters: These next-gen displays are improving clarity, performance, and portability — making them perfect for specialized workflows.
Choosing the Best Computer Monitor for You
In addition to the above monitor and panel types, there are a number of other factors that could determine the best display for you and your lifestyle.
Monitor Size
If you are a gamer or a professional photo or video editor, you may want to choose a larger-than-average LCD monitor.
Monitors come in all different sizes, ranging from less than 21 inches all the way to 32 inches and beyond.
Your Setup: Dual-Monitor?
Many users choose to go with a dual monitor setup. This means that two monitors are used together, typically arranged side by side, creating the illusion of an extremely large display area.

This setup is great for gaming and graphic designers. It can also be useful for programmers, as these users can rotate one monitor vertically, to better suit the programming application.
If you prefer a larger screen but don’t want two separate monitors, there are ultrawide monitors as well.
Summary: Which Monitor Type Is Right for You?
With so many options on the market, your monitor choice should reflect your lifestyle and professional needs. Use this quick guide:
| User Type | Recommended Monitor Type |
| Gamer | High-refresh TN, fast-response IPS, or G-Sync/FreeSync VA panels |
| Designer/Photographer | IPS or OLED panels with wide color gamut and 4K+ resolution |
| Office/Student | Affordable IPS or VA with eye-care tech and adjustable stands |
| Movie Enthusiast | Ultrawide VA or OLED displays with deep blacks and rich contrast |
| Programmer/Developer | Dual-screen setup or vertical monitor with anti-glare and crisp text |
Final Takeaway: Focus on resolution, panel type, refresh rate, and ergonomics based on what you use your screen for most — that’s how you find the best value.