Color depth, a crucial aspect of digital image quality, determines the range of colors a pixel can display. It’s measured in bits per pixel, influencing the color variety and image quality. Higher bit depths allow more color shades, enhancing the photorealistic quality of images. For instance, 24-bit color depth offers a wide gamut of colors, making it a standard in digital photography. Understanding color depth is essential for anyone working with digital images and offers enhanced visual quality to the best gaming monitors.
Key Takeaways_
- The availability of bit depth depends on the format of the file. For example, standard JPEG only uses 8-bits per channel.
- Each pixel in an image with greater color depth can display variations of a specific color.
- Using a camera that saves images in RAW format requires more space and system memory to store all the color variations.
Understanding Color Depth
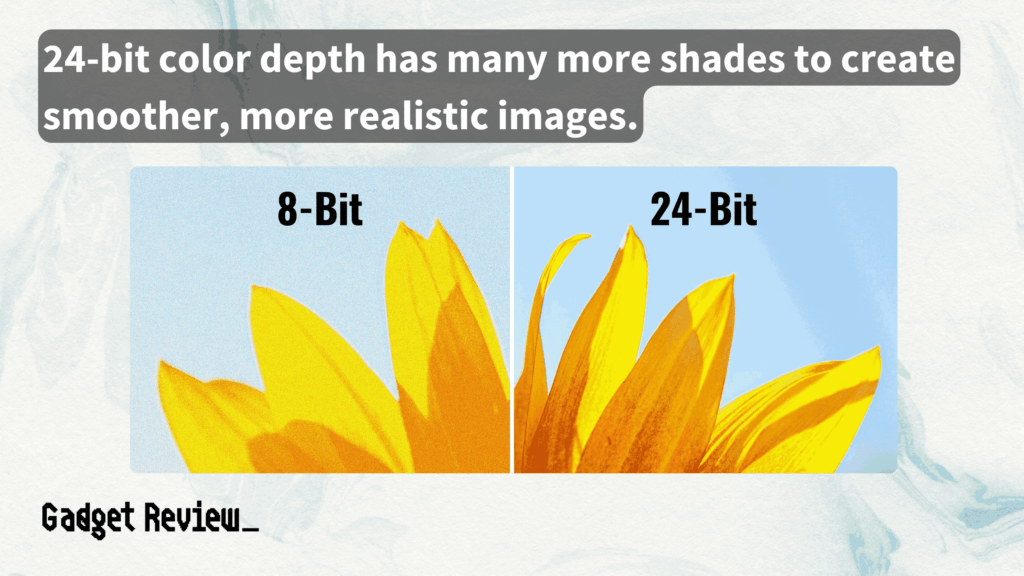
The first monitors and graphic cards to be designed supported only 1 bit – white and black colors. Most monitors on the market today offer at least 16.7 million colors which represent 32-bit.
Color depth, or bit depth, is fundamental in digital imaging. It refers to the number of bits used per pixel to represent color.
Each bit stores color data, with common standards being 8-bit, 10-bit, 24-bit, and 32-bit color depths. The term “True Color” often refers to 24-bit color, providing a broad spectrum of distinct colors.
In simpler terms, the higher the bit depth, the more color variations and smoother color gradients an image can display, leading to more accurate color representation.
insider tip
Color depth is a measurement that represents the number of colors a pixel of an image can show.
Monitors that have high pixel depth provide digital professionals with enough room to work on projects. In addition, these professionals can use aesthetically appealing options like transparency, shadows, and gradients to edit their content.
Technical Aspects of Color Depth
Diving deeper, color depth encompasses bits per channel and color channel concepts. Each primary color channel (red, green, blue) in an image file has a certain number of bits allocated.
For example, in 24-bit color depth, each channel gets 8 bits, allowing for 256 shades per channel. This results in millions of possible color combinations.
Higher depths like 32-bit include an alpha channel for transparency control. Understanding these technicalities is vital for professionals dealing with video signal processing or digital content creation.
While not entirely related to bit depth, you may also be interested in learning what size monitors pro gamers use.
Color Depth in Digital Displays
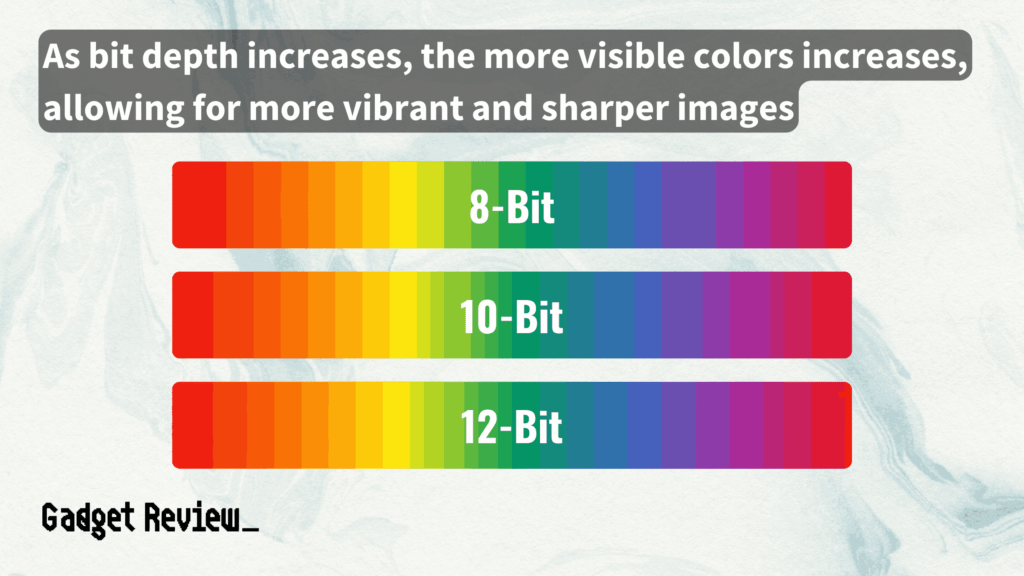
Modern displays and graphics cards play a significant role in color depth representation. They determine how well the color depth of files translates to visual output.
Higher bit depths like 10-bit and 12-bit are increasingly common in modern graphics cards, offering a wider range of colors and smoother transitions.
This is particularly important in high-end video production and gaming, where color accuracy and subtle gradations are key.
Just as color depth is important, you should also understand what nits brightness is for your display to ensure the screen can get bright enough for your environment.
insider tip
If your monitor has a higher color depth, it will be possible to see an image with better clarity and tone.
Unfortunately, some file formats like GIF only support 8-bit depth. Therefore, the limit on the number of colors on specific file formats cannot allow you to get the best image quality; this is true for the gif format.
Some display monitors can support color depth to a specific limit, like sRGB color space. For broader color space, compare DCI-P3 vs sRGB.
For example, you may have a high-quality image in 16-bit per channel RGB format, but the screen you are using to see the photo is only displaying to the 8-bit level. So, as you can see, there is a lot you need to consider before formatting images.
Bit depth is imperative because it represents the number of colors that you can see per pixel. If your monitor has a higher color depth, it will be possible to see an image with better clarity and tone.
A lot determines the quality of a photo, from color depth to the number of pixels in an image. So, if you want to produce photorealistic images and videos, you need to go for 24-bit color. You can get this level of color depth by using modern graphics cards.
What You Need to Know Before Changing Image Color Settings
Below is what you need to consider:
- Lots of the correction commands and effects only apply to higher color depth images. You can reduce the image’s color depth and save the work in another format once you finish working.
- File formats like GIFs limit the number of colors in the image to be displayed correctly on any monitor.
- The monitor settings and capabilities determine the color depth. For example, suppose you project an image with a higher color depth to a monitor with a lower color depth. In that case, the image will have some color distortion.
In practical terms, choosing the right color depth depends on the application.
For digital photography, 24-bit color depth is often sufficient. However, for professional video editing or graphics work, higher bit depths like 32-bit offer more flexibility.
STAT: The human eye discerns about 10 million colors. Therefore, anything more significant than 24bpp is too much if the purpose of the image is for viewing. However, images with higher than 24bpp are ideal for post-processing. (source)
It’s also important to consider file sizes; higher color depths result in larger files requiring more drive space.
Formats like RAW in photography offer a wider dynamic range, making them ideal for high-quality image processing.
In conclusion, color depth is a fundamental concept in digital imaging, affecting everything from file formats to the quality of video cards.
Understanding its technical aspects, from bits per pixel to color space, is essential for anyone working with digital images.
As technology advances, we’re seeing a transition to higher color depths, offering more color variations and smoother color gradients, enhancing the overall visual experience.