Humanoid and animal-like robots are revolutionizing the field of robotics with their impressive capabilities. From the lightning-fast Cheetah by Boston Dynamics to Honda’s E2-DR, designed for disaster response, and Engineered Arts’ Ameca, which excels in human interaction, these robots are poised to transform various industries. This list highlights their unique features, current development status, and the potential impact they may have on our daily lives and society.
1. Atlas

Atlas, developed by Boston Dynamics, is a bipedal humanoid robot designed for dynamic movements such as parkour, running, and even backflips. Equipped with advanced sensors, including Lidar and stereo vision, Atlas can perform tasks that require dexterity and agility. It represents a significant leap in humanoid robotics, showcasing the potential for robots to assist in complex and hazardous environments.
The latest iteration of Atlas, unveiled in 2024, is fully electric and designed for industrial and logistics applications. This new version is stronger, more dexterous, and more agile than its predecessors, marking a shift from research to practical, real-world applications. Atlas continues to push the boundaries of what’s possible in robotics, paving the way for future advancements in human-robot collaboration.
2. Sophia
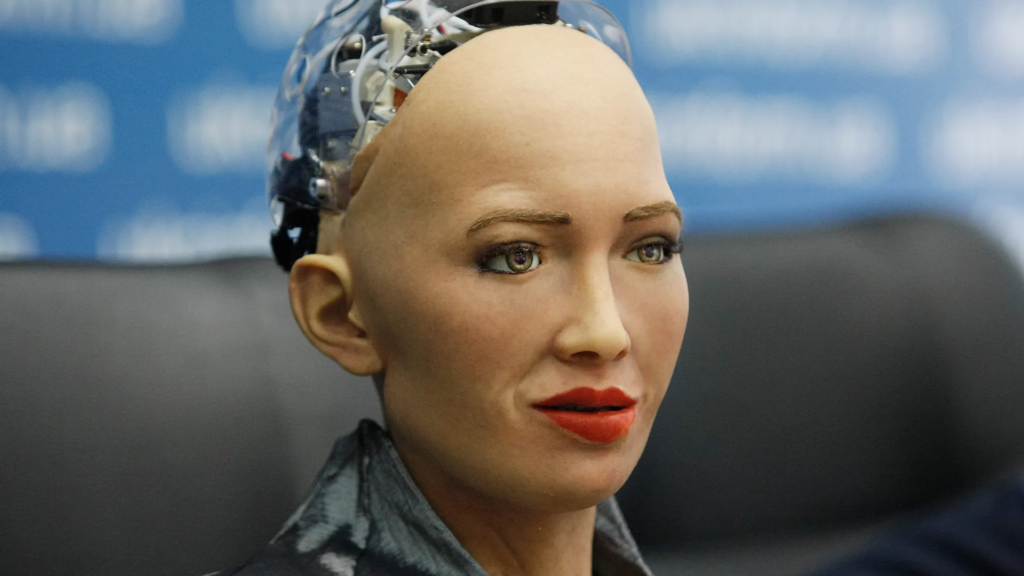

Sophia is a humanoid robot developed by Hanson Robotics, known for its lifelike appearance and ability to engage in conversations using advanced AI and facial recognition. It has been used to demonstrate the potential of AI in social interactions, healthcare, and education, making it a symbol of human-robot interaction.
Sophia is still active, with ongoing developments in AI and potential applications in various fields. Hanson Robotics continues to enhance Sophia’s capabilities to interact more naturally with humans, exploring new ways to integrate AI-powered robots into society and pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in human-robot communication.
3. ASIMO
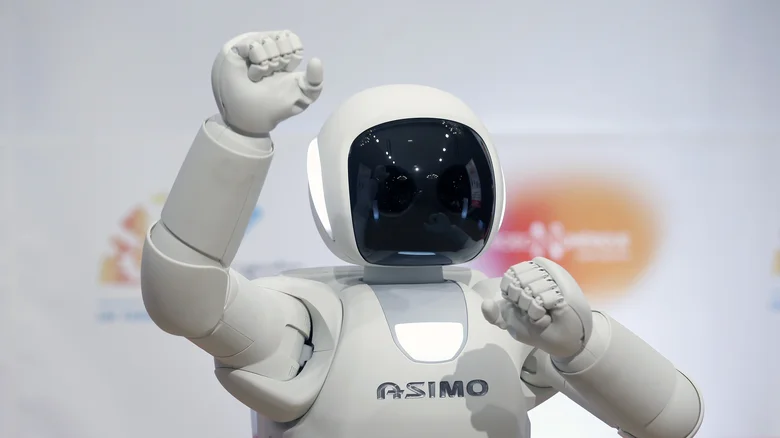

ASIMO, developed by Honda, is a humanoid robot designed to assist with mobility. It can recognize faces, gestures, and sounds, and navigate autonomously. ASIMO was one of the first robots to demonstrate advanced bipedal locomotion and human-robot interaction, paving the way for future developments in assistive robotics.
Although Honda officially retired ASIMO in 2018, the company continues to apply its technologies in other robotics projects, focusing on mobility assistance devices and autonomous vehicles. The legacy of ASIMO lives on in these new innovations, influencing the development of robots designed to enhance human mobility and independence.
4. Snakebot
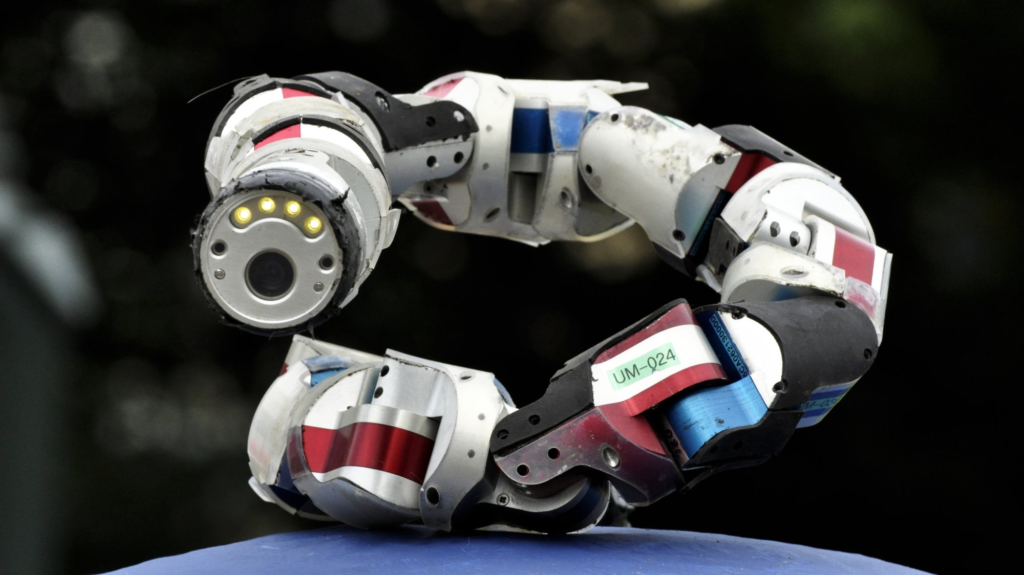

Snakebot, developed by Carnegie Mellon University, mimics the movements of a snake, allowing it to climb, swim, and navigate through tight spaces. This unique design makes it ideal for search and rescue missions, exploration, and even surgical applications, where flexibility and maneuverability are crucial.
The Snakebot project is still active, with ongoing research and development to enhance its capabilities for various applications. Its ability to traverse challenging terrains and access confined spaces positions it as a valuable tool in both emergency situations and specialized medical environments.
5. Moley – Robot Kitchen
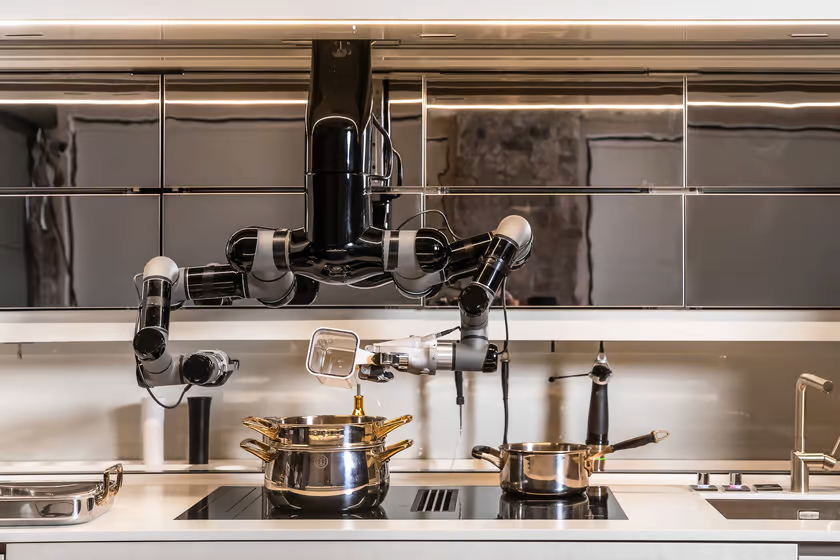

Moley Robotics’ Robot Kitchen is an AI-driven robot capable of preparing and cooking meals by mimicking the movements of a human chef. This innovation could revolutionize home cooking by providing a fully automated kitchen assistant, reducing the time and effort required for meal preparation.
Moley Robotics continues to develop and refine the Robot Kitchen, working towards commercial release. As the technology advances, it holds the promise of transforming how we approach cooking and meal preparation in our daily lives.
6. Robotic Seagull
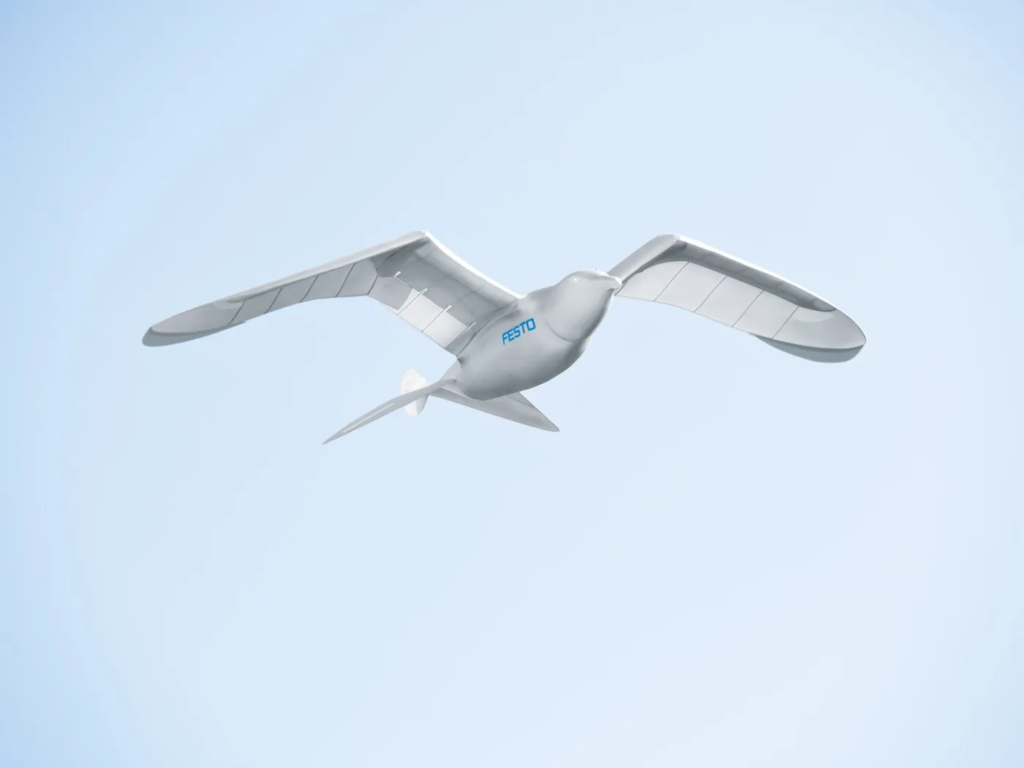

Developed by Festo, the Robotic Seagull mimics the flight of a real seagull, capable of autonomous takeoff, landing, and mid-flight course changes. This robot showcases advancements in biomimicry and could be used for environmental monitoring and research.
While the specific seagull project may not be actively developed, Festo continues to innovate with nature-inspired robots. The principles learned from the Robotic Seagull can inform future designs in aerial robotics and environmental applications.
7. Digit
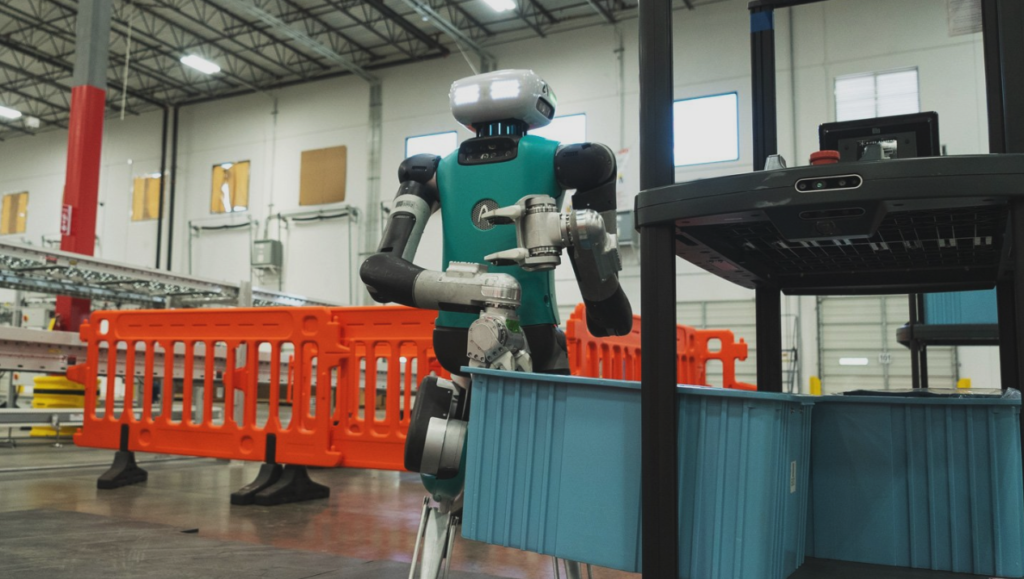

Digit, from Agility Robotics, is a humanoid robot designed for dynamic movement, capable of walking, climbing stairs, and navigating unstructured environments. Its versatility makes it suitable for logistics and warehouse operations, where adaptability is key.
Digit is still in active development, with significant funding and partnerships, including with Amazon, to develop it for commercial applications. As it evolves, Digit has the potential to streamline operations in various industries, improving efficiency and safety.
8. Pepper
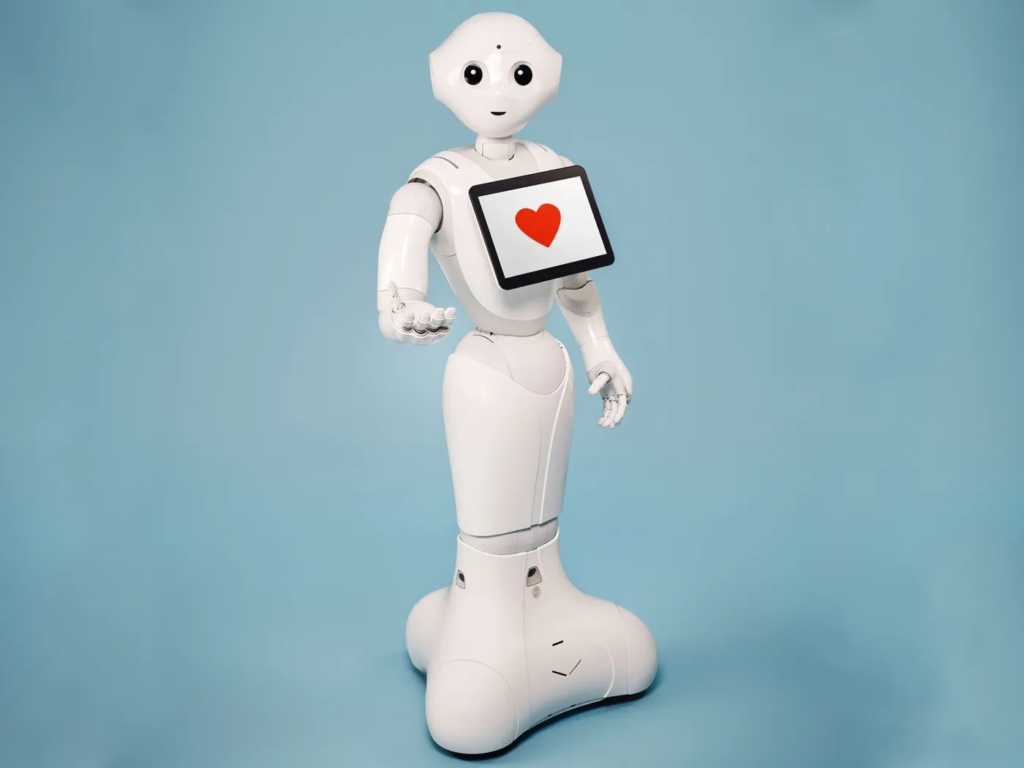

Pepper, developed by Softbank Robotics, is a humanoid robot capable of recognizing human emotions and engaging in conversations. It has been used in retail, healthcare, and education, demonstrating the potential for robots to enhance human-robot interaction in various settings.Pepper is still active, though production was temporarily halted in 2021. Softbank Robotics continues to support existing units and develop next-generation social robots, aiming to improve the ways robots can assist and engage with people.
9. Stuntronic Robot
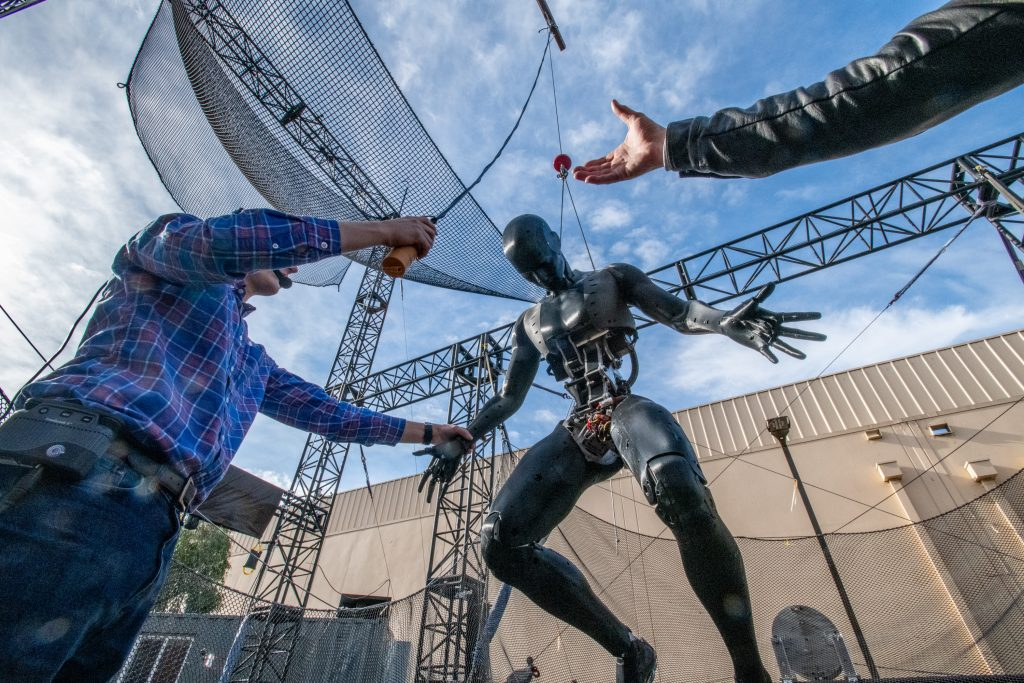

Disney’s Stuntronic Robots are animatronic stunt doubles capable of performing dynamic aerial maneuvers like flips and twists. These robots could revolutionize entertainment by providing realistic and safe stunt performances in theme parks and films.
The Stuntronic project is ongoing, with continuous development for potential use in Disney’s entertainment productions. As these robots become more refined, they could set new standards for live performances and cinematic stunts.
10. Chip
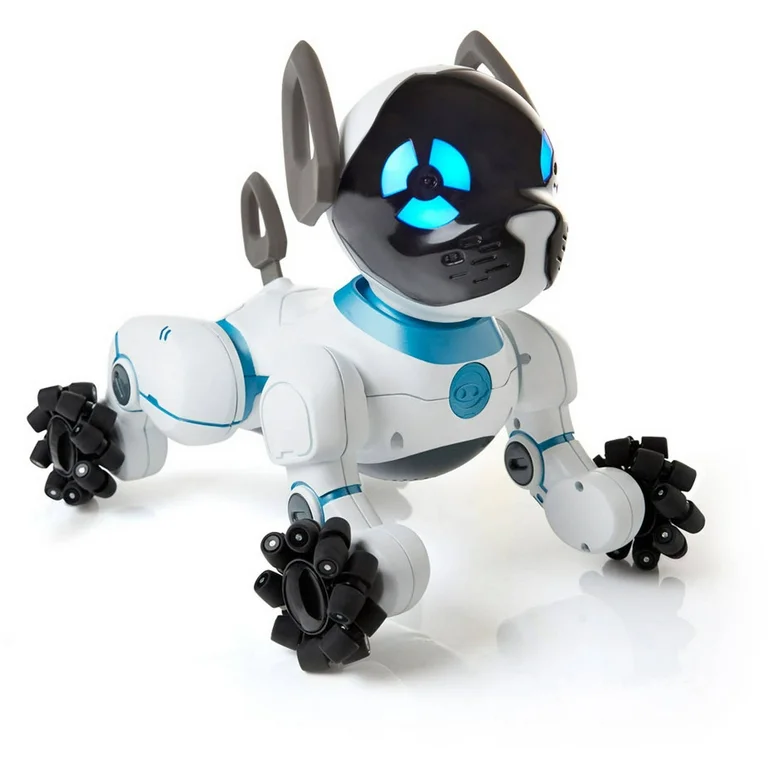

Chip is a robotic dog equipped with advanced sensors for spatial awareness, capable of playing fetch, following commands, and docking itself for charging. This robot offers a glimpse into the future of robotic pets, providing companionship and entertainment with advanced AI capabilities.
The status of Chip is unclear, as the original company, WowWee, has shifted focus to other toy products. It remains uncertain if Chip is still in production or development, but its concept highlights the growing interest in robotic companions.
11. Injectable Nanobots
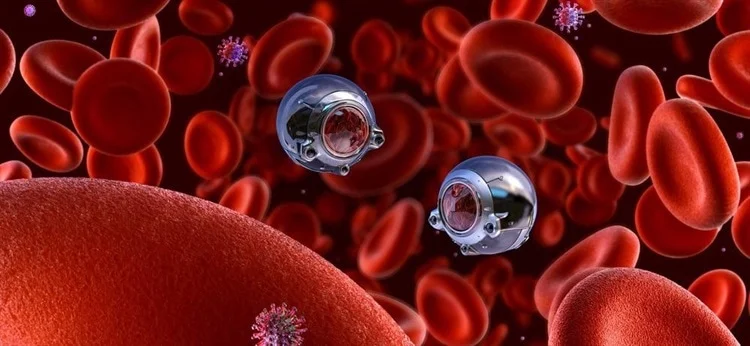
Developed at Cornell University, these tiny injectable nanobots can walk around inside the human body, potentially delivering drugs to specific sites. This technology could revolutionize medicine by providing targeted drug delivery and minimally invasive treatments.
Research on injectable nanobots continues, with ongoing development for potential medical applications. As this field advances, it holds the promise of transforming how we approach treatment and patient care in the medical field.
12. Spot the Robo-Dog
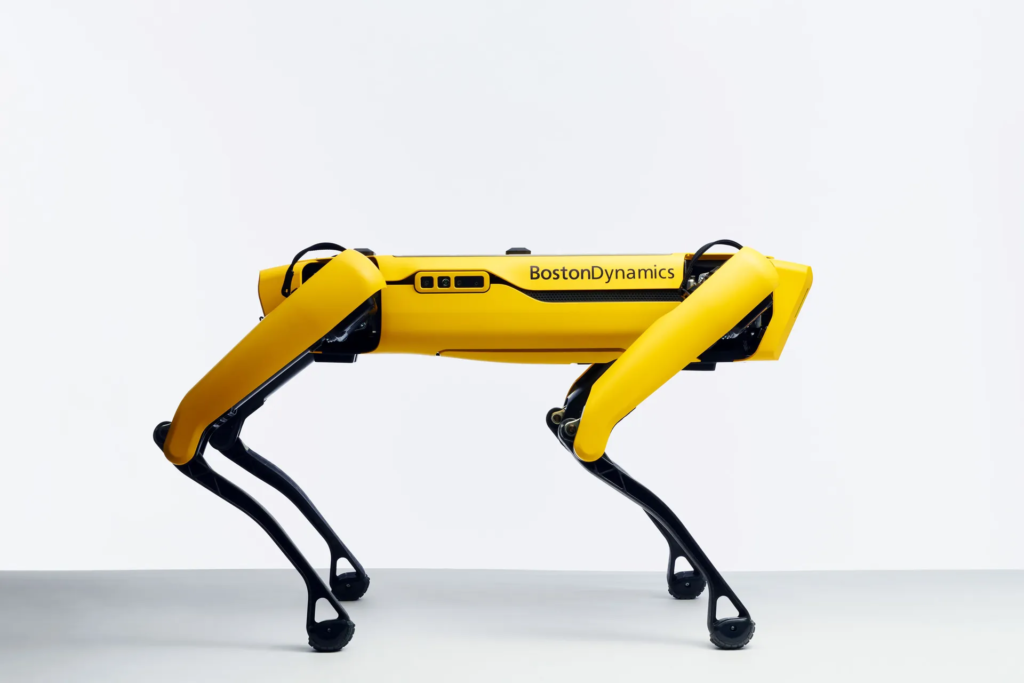

Spot, another creation by Boston Dynamics, is a versatile quadruped robot used in various industries for inspection, data collection, and more. Its ability to navigate rough terrains and perform tasks in hazardous environments makes it valuable for construction, healthcare, and public safety.
Spot is actively being developed and commercialized, available for purchase and used in various industries. Its deployment across different sectors demonstrates the growing acceptance and utility of robotics in everyday operations.
13. Weed-Killer Robot
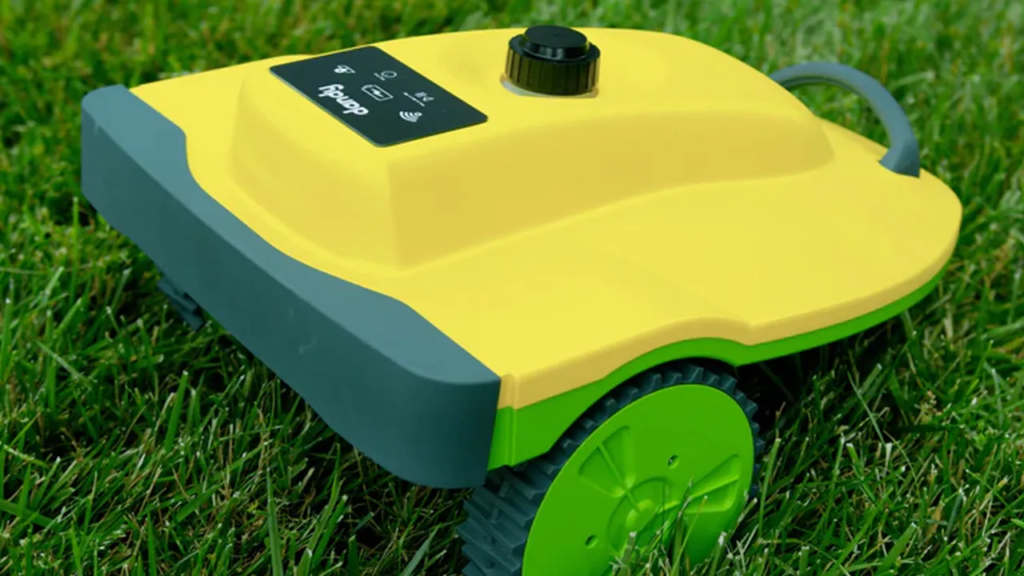

Autonomous weed-killing robots, like those developed by Carbon Robotics, use high-powered lasers to eradicate weeds without disturbing the soil. This technology could revolutionize agriculture by reducing the need for herbicides and promoting healthier crops.
These robots are commercially available and actively being improved for agricultural use. Their implementation represents a shift towards more sustainable farming practices, addressing environmental concerns while enhancing crop management.
14. Vyommitra

Vyommitra is a half-humanoid robot developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) for space missions, capable of operating switch panels and interacting with astronauts. This robot could assist in space exploration by performing tasks that are dangerous or tedious for human astronauts.
Vyommitra is still in active development, with plans to use the robot in upcoming uncrewed space flights. Its advancements could play a crucial role in future missions, enhancing safety and efficiency in space exploration.
15. Boston Dynamics’ Cheetah
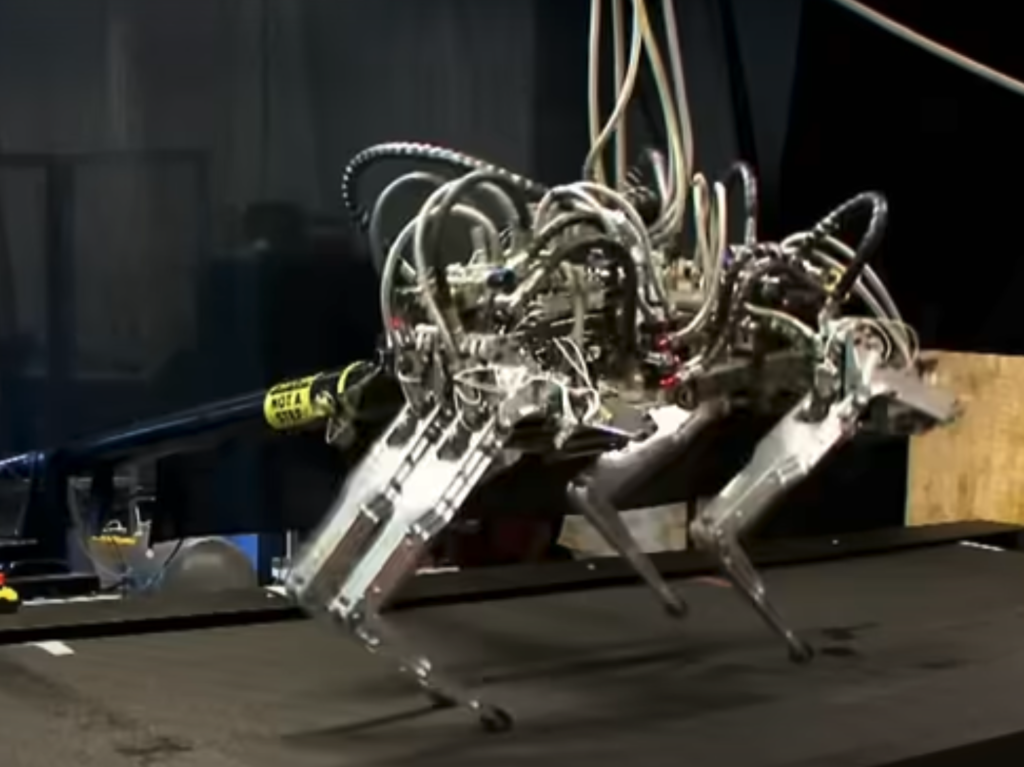
Boston Dynamics’ Cheetah is a quadrupedal robot designed to mimic the running motion of a cheetah. It can reach speeds of up to 28 mph (45 km/h), making it the fastest-legged robot in the world. The Cheetah’s flexible spine and articulated head allow it to stretch and contract with each stride, much like its biological counterpart.
While the original Cheetah was tethered to an external power source, Boston Dynamics has since developed untethered versions like WildCat and Spot. These robots showcase advancements in dynamic locomotion and have potential applications in search and rescue, military operations, and exploration of hazardous environments.
16. Honda’s E2-DR
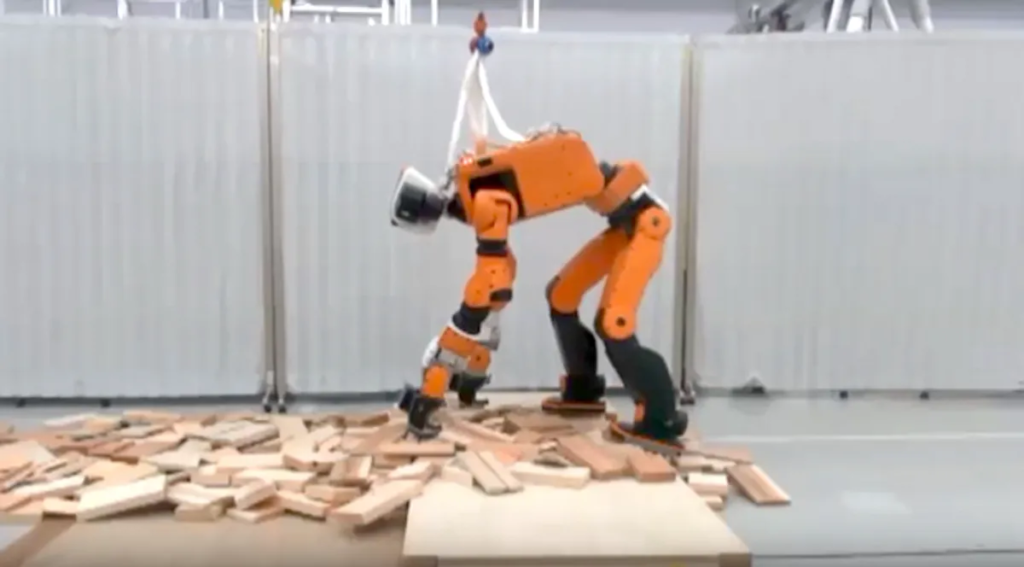

Honda’s E2-DR is a disaster response humanoid robot designed to operate in environments too dangerous for humans. Standing at 1.68 meters tall and weighing 85 kg, E2-DR can navigate through narrow spaces, climb ladders, and crawl through debris. Its waterproof and dust-resistant design allows it to function in harsh conditions.
While Honda has not released recent updates on E2-DR, the robot represents significant progress in creating humanoid machines capable of assisting in disaster scenarios. The technologies developed for E2-DR continue to influence the field of robotics, particularly in the areas of mobility and environmental adaptability.
17. Engineered Arts’ Ameca

Engineered Arts’ Ameca is a humanoid robot designed to showcase the latest advancements in human-robot interaction. With highly expressive facial features and fluid body movements, Ameca can convey a wide range of emotions and engage in natural conversations. The robot’s AI-powered responses and ability to recognize and react to human expressions make it a pioneer in social robotics.
Ameca is actively being developed and improved, with potential applications in customer service, education, and entertainment. As the technology evolves, Ameca and similar robots could play significant roles in enhancing human-robot communication and integration in various social settings.