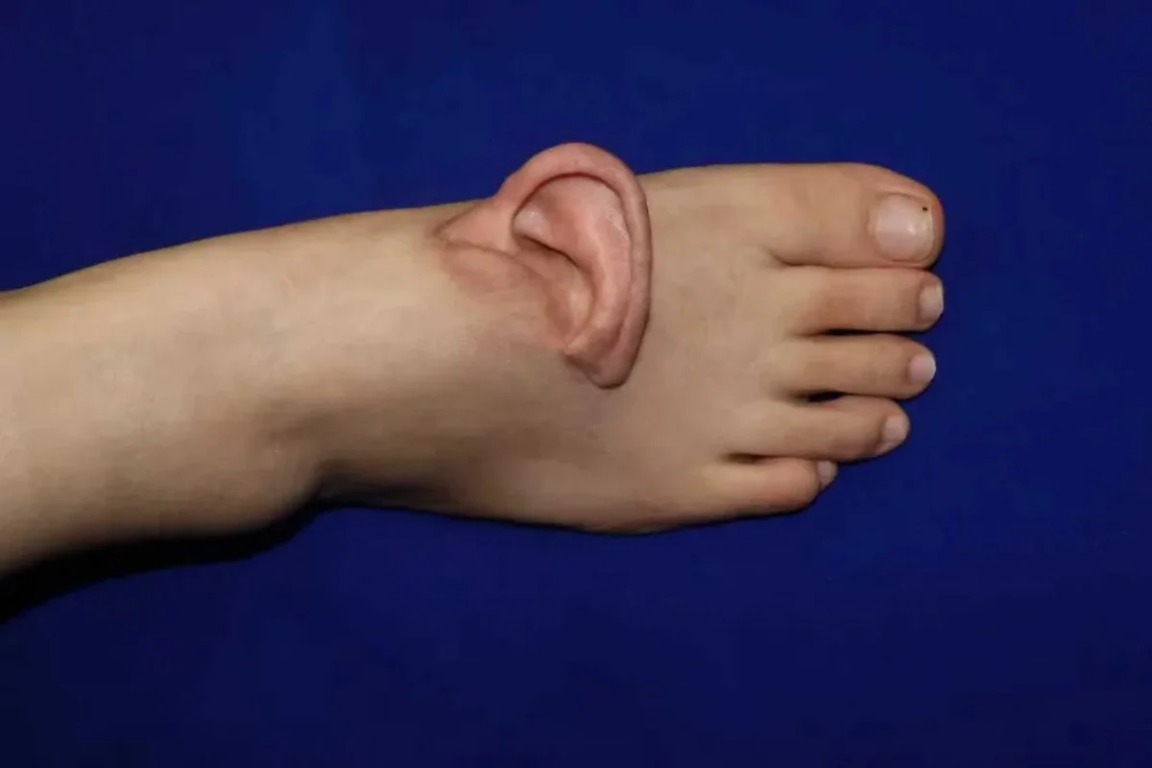
Microsurgery just achieved what seemed impossible: Chinese surgeon Qiu Shenqiang successfully grafted a human ear onto a patient’s foot as a life-saving reconstructive measure. The procedure, performed using heterotopic grafting techniques, represents a significant advancement in microsurgical reconstruction.
While details about the specific medical circumstances remain limited, this case demonstrates how far surgical innovation has pushed the boundaries of what’s possible in reconstructive medicine. The successful integration challenges traditional thinking about anatomical placement during complex reconstructive procedures.
Revolutionary Surgical Technique Defies Convention
The heterotopic grafting method allows surgeons to grow replacement tissue in unexpected locations.
Heterotopic grafting sounds like science fiction, but it’s becoming surgical reality. The technique involves transplanting tissue to a location different from its original anatomical position—in this case, placing an ear on the foot where blood supply and healing conditions prove optimal.
Think of it like growing a backup organ in your body’s most hospitable environment before moving it to its final destination. This approach gives surgeons unprecedented flexibility when traditional reconstruction sites lack adequate blood supply or have suffered extensive damage.
Patient Care Meets Surgical Innovation
The procedure prioritizes function and healing over conventional anatomical placement.
Your foot might seem like an odd choice for ear reconstruction, but it offers rich blood supply and stable tissue environment crucial for graft survival. The surgical team chose this location to ensure the grafted ear receives optimal nourishment during the critical healing phase.
This isn’t permanent placement—the ear will eventually be repositioned to its proper anatomical location once fully integrated and healed. The patient’s recovery timeline and specific medical needs determined this unconventional but medically sound approach.
Implications for Future Reconstructive Surgery
This case could reshape how surgeons approach complex reconstruction challenges.
Medical teams worldwide are watching cases like this closely. The success of heterotopic grafting techniques could revolutionize treatment for patients requiring complex reconstructive surgery after trauma, cancer, or congenital conditions.
Dr. Qiu’s work demonstrates that surgeons no longer need to limit themselves to traditional anatomical constraints when patient outcomes depend on creative solutions. This represents the kind of surgical thinking that transforms medicine—prioritizing what works over what looks conventional.
The procedure showcases medicine’s evolution toward personalized, innovative solutions that put patient outcomes above surgical tradition. As microsurgical techniques continue advancing, expect more cases that challenge our assumptions about what’s possible in reconstructive medicine.