In tech, breakthroughs are happening at lightning speed, transforming everything from healthcare to space travel. Below, we’ve rounded up 19 of the most mind-blowing innovations that are turning science fiction into reality, pushing boundaries in medicine, transportation, and sustainability.
19. 3D-Printed Heart
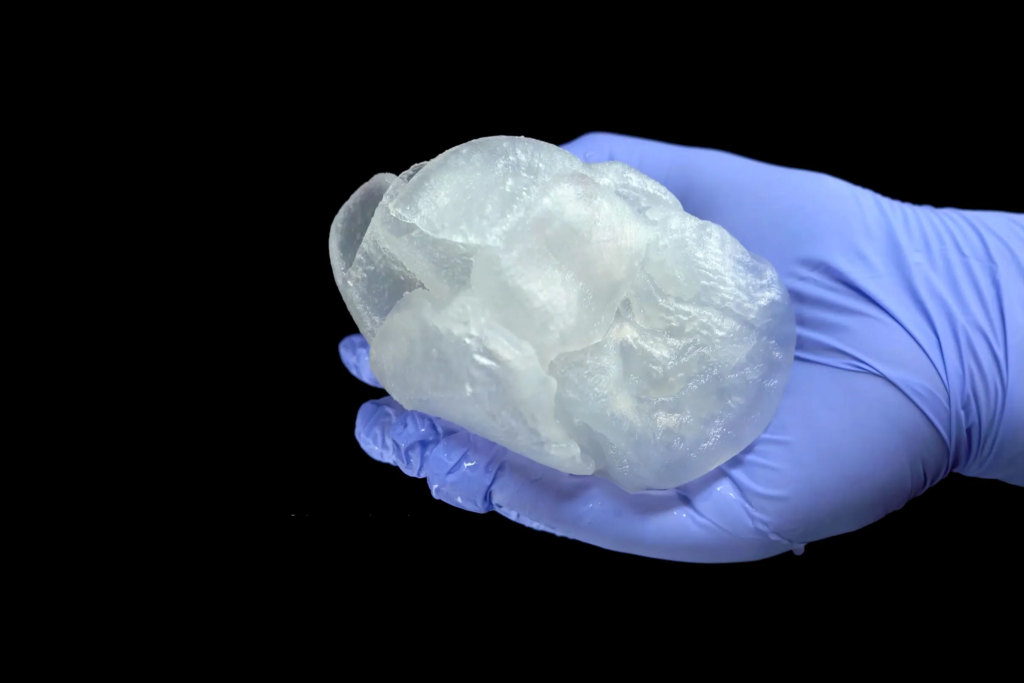
In 2019, researchers at Tel Aviv University made headlines by 3D-printing a miniature human heart. Using bio-ink derived from human stem cells, they created a small-scale, functioning heart, complete with chambers and blood vessels. While it doesn’t fully beat on its own just yet, this innovation hints at a future where we could 3D-print fully functioning human organs, easing the demand for donor hearts. Imagine a world where organ transplants are custom-built to suit each patient, minimizing rejection risks and sidestepping long waiting lists. It’s early days, but this could redefine how we treat heart disease.
18. Prosthesis Exoskeleton
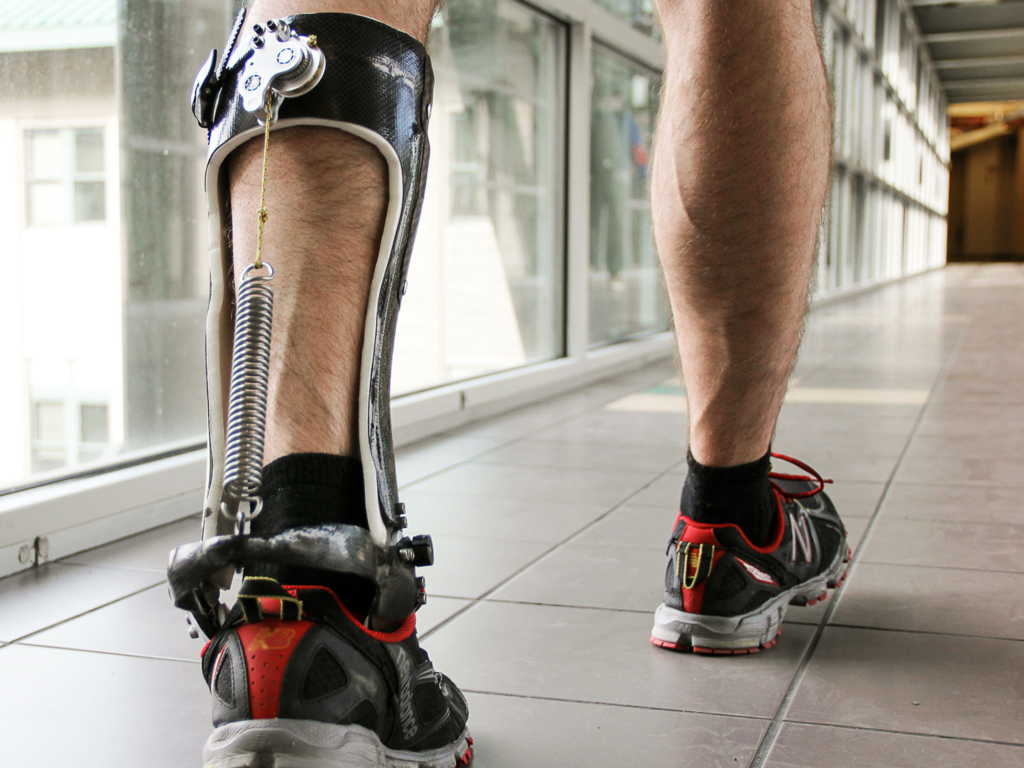
Exosapien Technologies is reimagining wearable robotics with Prosthesis, a 14-foot-tall, 9,000-pound exoskeleton that makes the stuff of sci-fi a reality. This human-controlled mech can run and traverse rugged terrains, boasting 200 horsepower of electric motor-driven power. Beyond the potential for sports and entertainment, this kind of tech could have real-world applications in construction or emergency response, where it could boost human strength to superhuman levels. Prosthesis is more than a futuristic gadget; it’s a glimpse of how machinery and human skill could blend seamlessly.
17. Micro-Robots

Northwestern University engineers developed what might be the world’s tiniest robots—microscopic crabs that are just 1/50th of an inch wide. Built from shape-memory alloys that flex when heated, these tiny bots walk using a scanning laser beam. Their potential is huge: they could perform minimally invasive medical procedures, like unclogging arteries, or assist in assembling intricate components. It’s a step forward in precision tech, where these little guys can go places bigger robots just can’t reach.
16. Ferrofluid

Ferrofluid defies the laws of matter—it’s both liquid and magnetic. Invented in the 1960s by NASA for zero-gravity fuel management, it’s since found uses in audio equipment and machinery. The future? Imagine using ferrofluid to deliver drugs directly to specific body parts, reducing side effects and boosting treatment effectiveness. Its ability to transform under magnetic fields opens the door to endless possibilities in both technology and medicine.
15. City Glider Shoes

The City Glider Shoes, designed by Frederick Phua, take walking to a whole new level. These innovative kicks use hydraulic pistons to convert each step into forward momentum, making it easier to walk long distances, especially in urban environments. Crafted from lightweight materials like carbon fiber, these shoes offer comfort and shock absorption. If they hit the market, they could make walking not just sustainable but genuinely enjoyable, cutting back on short car trips and keeping people moving.
14. Magnetic Confinement Fusion (Tokamak)
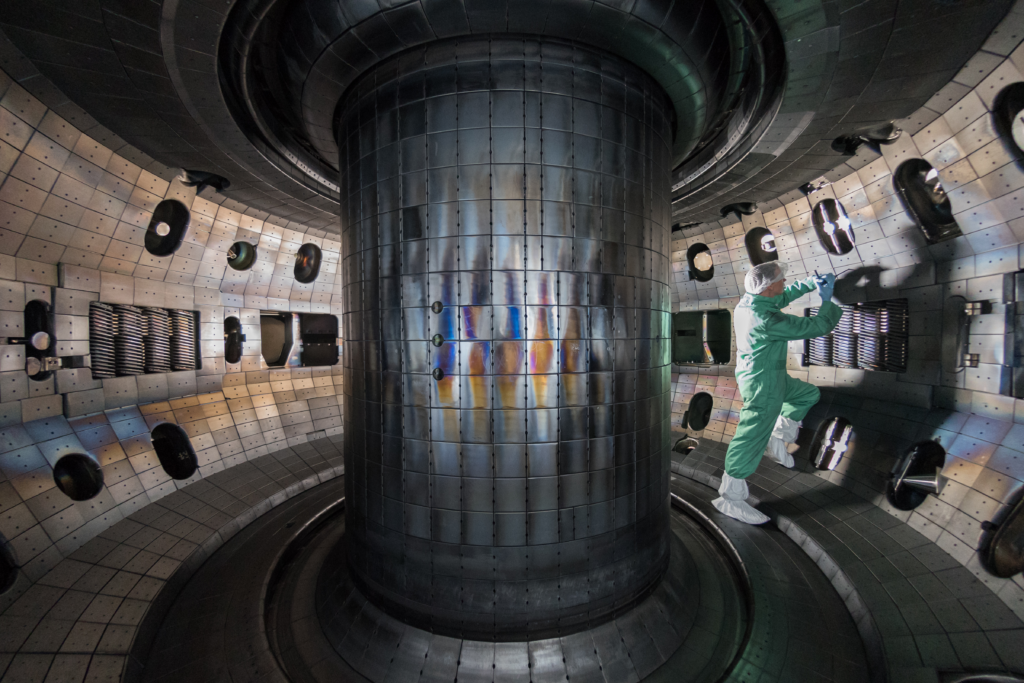

Tokamaks aim to harness the power of the stars, using magnetic fields to contain plasma and trigger fusion—the holy grail of clean energy. With new superconducting magnets developed at MIT, the prospects for sustained fusion are looking up. The International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER), set to launch in 2025, is the next big hope. If successful, we’re talking about an almost limitless, clean energy source that could help us kick our fossil fuel habit for good.
13. Aeroponics
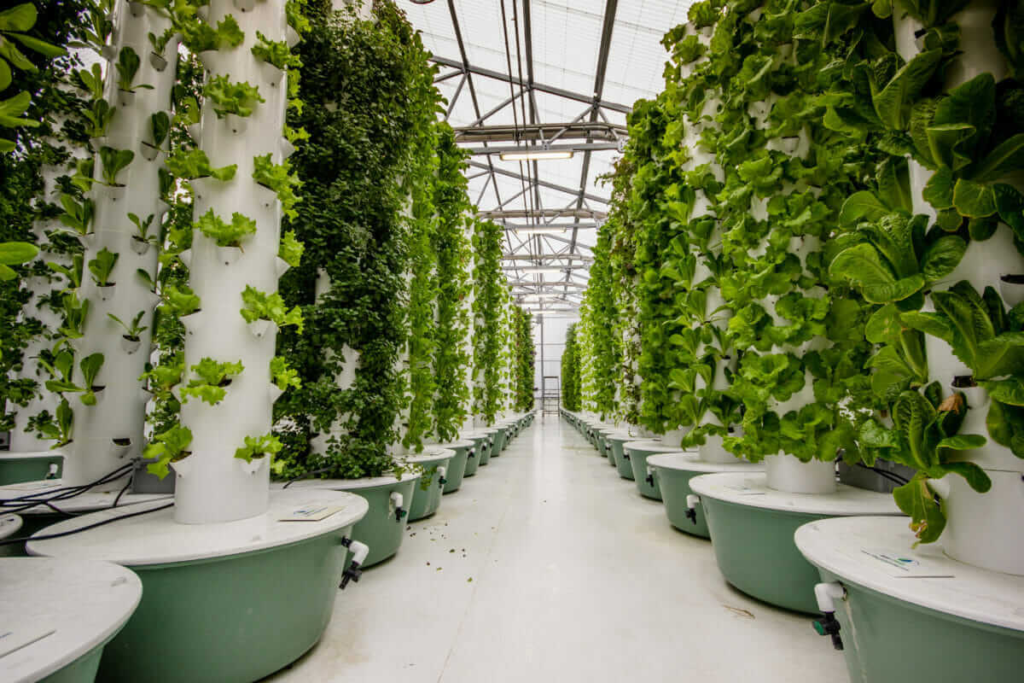

Say goodbye to soil. Aeroponics grows plants by suspending them in air and misting their roots with nutrients, reducing water usage by up to 90%. This method allows for faster growth and can be set up just about anywhere—think urban farms or even space missions. NASA is working on compact aeroponic systems to sustain astronauts on long trips to Mars, proving that this could be the future of agriculture, both on Earth and beyond.
12. DuoSkin and SkinKit

DuoSkin, from MIT and Microsoft, turns your skin into an interactive device using ultra-thin, temporary electronic tattoos. Acting as a touchpad or remote control, DuoSkin is futuristic but temporary. Enter SkinKit, developed at Cornell—these are reusable electronic tattoos that can monitor health metrics or provide navigation assistance. This blend of tech and skin could make wearable devices as we know them obsolete, offering more natural interaction with our digital world.
11. Cyborg Insects

Researchers in Japan have turned cockroaches into tiny cyborgs, equipping them with solar-powered control modules. These remote-controlled bugs can navigate disaster zones too dangerous for humans, potentially aiding in search-and-rescue missions. While it sounds a bit like a sci-fi movie plot, this technology shows how blending biology with robotics can lead to new, life-saving applications.
10. The Ark (Floating Hotel)

Designed to float and function off the grid, The Ark is an eco-friendly hotel concept from Remistudio. Equipped with solar panels, wind turbines, and rainwater collection systems, it’s built to withstand rising sea levels. This floating sanctuary could offer a solution to climate change challenges in coastal areas, blending luxury with resilience.
9. UltraFan Jet Engine
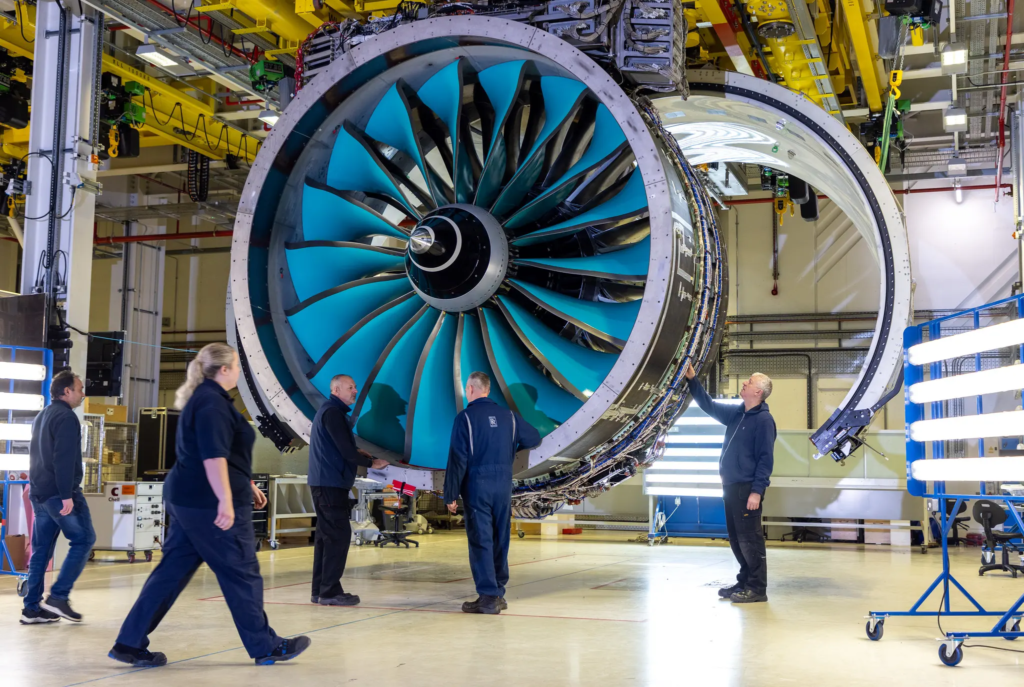

Rolls-Royce’s UltraFan engine is changing the aviation game, providing 10% better fuel efficiency compared to older models while being quieter and cleaner. It’s a step forward for more sustainable air travel, showing how industry giants are prioritizing the environment without sacrificing performance.
8. Graphene Gyroids

Imagine a material stronger than steel but 95% lighter. That’s graphene gyroids—3D structures designed by MIT using the super-strong, ultra-light material graphene. The challenge? They’re expensive to produce, but as technology advances, they could revolutionize construction and aerospace with unparalleled strength-to-weight ratios.
7. Hyperloop and Maglev Trains

The Hyperloop concept, boosted by magnetic levitation, promises train travel at speeds up to 750 mph. Though still in development, maglev technology is already propelling trains in countries like Japan. This could mean faster, quieter, and more energy-efficient transport options in the future.
6. The Float (Maglev Car Concept)
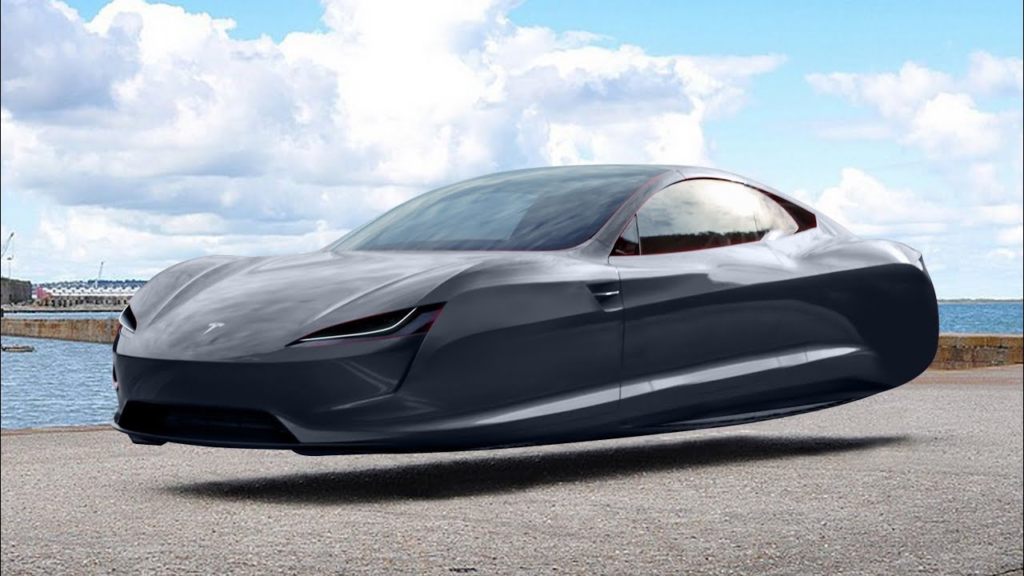

The Float is a maglev concept car that doesn’t drive—it hovers. These bubble-like vehicles use magnetized tracks to glide without friction. While it’s purely conceptual for now, The Float challenges how we think about transportation, potentially reducing road wear and cutting down on energy usage.
5. MONOCAB Rail Project

MONOCAB is a German project breathing new life into abandoned railways with self-driving, single-cabin vehicles. These app-summoned pods could offer rural communities a sustainable alternative to traditional public transit, using existing tracks to reduce environmental impact.
4. Generative AI (ChatGPT, DALL-E)

AI tools like ChatGPT and DALL-E are revolutionizing content creation, design, and data analysis. While they improve productivity, their rapid growth raises questions about job security and the ethics of AI-generated content. Balancing AI’s capabilities with societal needs will be key as these technologies become more entrenched.
3. Electronic Skin Sensors
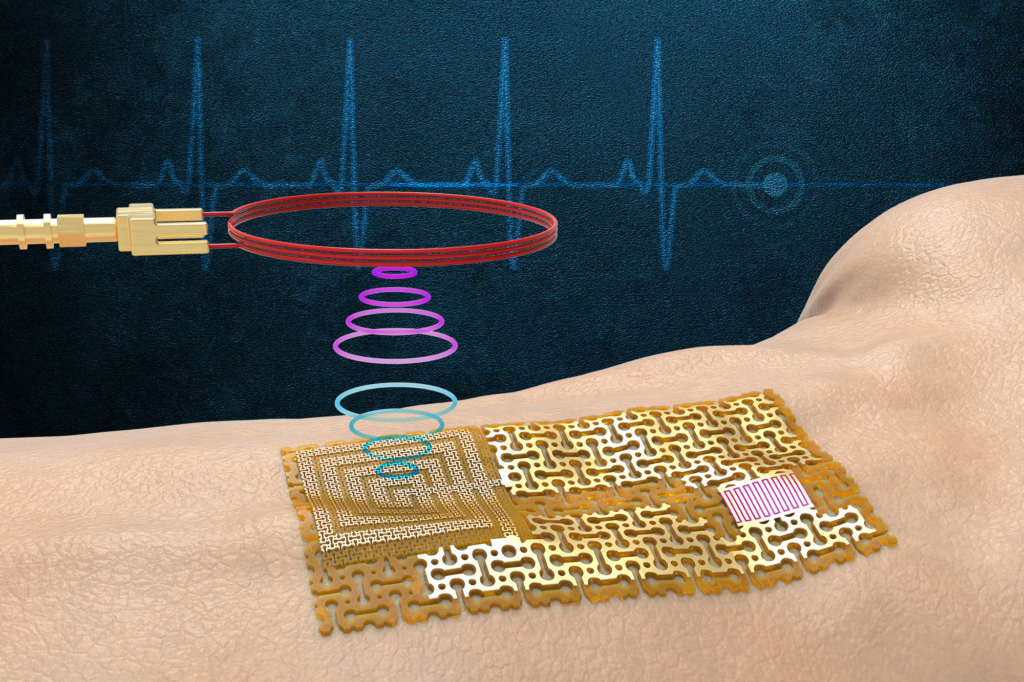
Skin sensors, like SkinKit, take wearables to a new level, offering lightweight, versatile devices that monitor health or provide sensory aids. Whether you’re tracking athletic performance or improving navigation, these devices seamlessly blend tech with the human body.
2. Flaming Fury Jet Engines

Modern jet engines, like the UltraFan, are more than just powerful—they’re sustainable. By integrating eco-friendly fuels and adaptive sensors, these engines balance high performance with reduced emissions, setting a new standard for aviation.
1. Cosmic Cultivation for Space

NASA’s aeroponic farming tech is more than just a futuristic idea—it’s a potential lifeline for long-term space missions. By providing fresh food with minimal resources, these systems could support human life on Mars or the Moon, laying the groundwork for sustainable off-planet living.