The global truck engine landscape spans decades of engineering evolution, from mechanical workhorses to modern electronic marvels. This ranking evaluates power, reliability, maintenance requirements, and real-world performance across commercial, off-road, and heavy-duty applications. Some engines earned legendary status through sheer durability, while others promised the moon but delivered expensive headaches. Here’s how twenty notable truck engines stack up when the marketing hype fades and actual performance takes center stage.
Btw, if you’re traveling this summer (or now) you might want to check out this VPN deal from Surfshark. Right now it’s $1.89/month + 4 months free (exclusive to GR readers).
20. International DT466E (1994-2003)

A diesel that taught fleet managers the true meaning of buyer’s remorse.
The DT466E looked promising on paper with electronic controls and 210-250 horsepower, but reality delivered a different story. Injector failures plagued these engines like a recurring nightmare, often requiring complete rebuilds before 150,000 miles. High-pressure oil pump issues created additional maintenance headaches that made accountants weep. While International fixed many problems in later iterations, the early DT466E earned its reputation as a money pit on wheels.
19. Ford 6.4L Power Stroke (2008-2010)

Short-lived and expensive—like that designer coffee habit you can’t afford.
Ford’s 6.4L Power Stroke promised 350 horsepower and cleaner emissions but delivered catastrophic reliability issues instead. The dual-turbo setup created impressive power when working, but catastrophic failures often occurred before 100,000 miles. Diesel particulate filter problems, turbocharger failures, and fuel system issues made this engine a warranty nightmare. Ford wisely discontinued it after just three years, but the damage to their diesel reputation lingered much longer.
18. GMC 702 V12 (1960s-1970s)

Twelve cylinders of automotive ambition that reality couldn’t quite support.
The 702 V12 represented GM’s attempt to dominate heavy-duty trucking with raw displacement and cylinder count. This massive engine produced respectable power for its era but consumed fuel like a small aircraft and required constant attention. Complex valve trains and accessibility issues made routine maintenance a technician’s workout routine. While historically significant, the 702 proved that more cylinders don’t always equal better results in commercial applications.
17. Mercedes OM352 (1960s-1980s)
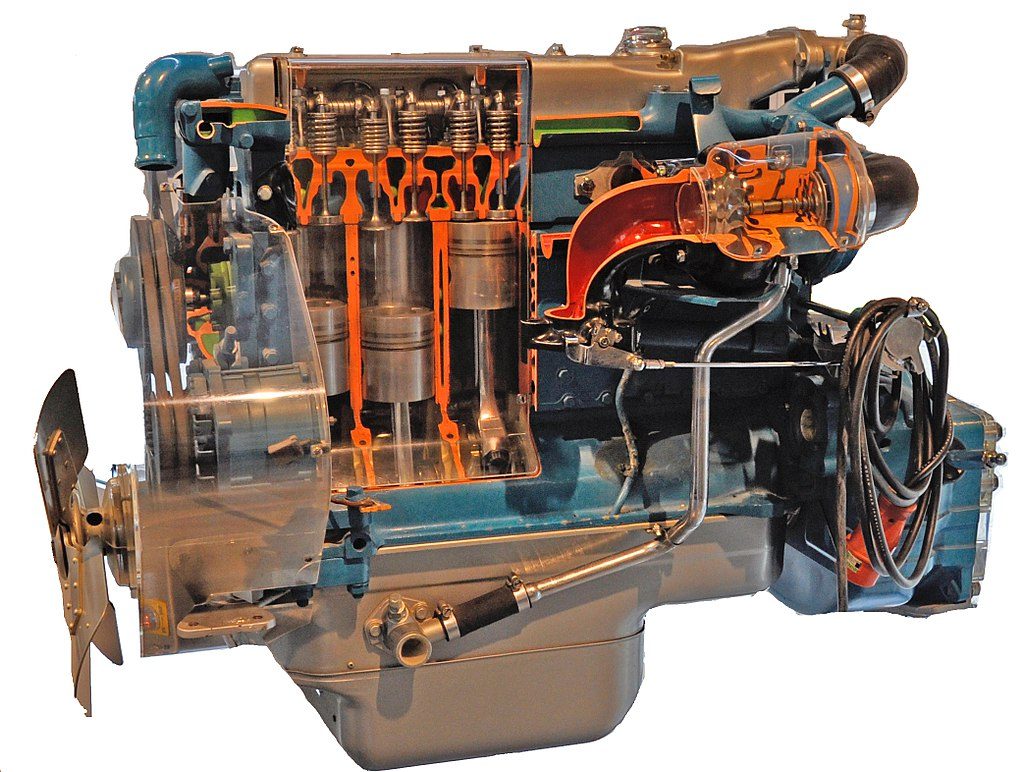
German engineering meets real-world durability—with mixed results.
The OM352 powered thousands of European trucks and buses with typical Mercedes precision engineering. This naturally aspirated diesel produced reliable power and featured robust construction that suggested longevity. However, parts availability outside Europe created headaches for international operators, and performance felt sluggish compared to turbocharged competitors. The engine earned respect for build quality but struggled with modern power demands as trucking evolved.
16. Volvo D12 (1990s-2000s)

Scandinavian reliability with a side of electronic complexity.
Volvo’s D12 brought sophisticated electronic controls and impressive fuel economy to long-haul trucking. The 12.1-liter inline-six produced competitive power while maintaining Volvo’s reputation for driver comfort and safety integration. Electronic issues occasionally frustrated technicians, and parts costs reflected premium European pricing. Despite these concerns, the D12 established Volvo as a serious contender in North American trucking markets.
15. Mack E7 (1980s-2000s)

The bulldog badge carried serious bite with this mechanical workhorse.
Mack’s E7 series represented old-school American truck engineering with mechanical injection and proven durability. These engines powered everything from garbage trucks to long-haul rigs with 300-400+ horsepower depending on configuration. Maintenance remained straightforward thanks to mechanical controls, though fuel economy lagged behind electronically controlled competitors. The E7 earned respect from owner-operators who valued simplicity over sophistication.
14. Detroit Diesel 8V92 (1970s-1990s)

Two-stroke thunder that announced its presence three counties away.
The 8V92 delivered unmistakable Detroit Diesel character with its distinctive two-stroke exhaust note and impressive power output. This V8 configuration produced strong acceleration and excellent cold-weather starting capabilities. However, fuel consumption rivaled small countries’ oil imports, and emissions regulations eventually spelled doom for the two-stroke design. Mechanics either loved or hated working on these engines—there was no middle ground.
13. Isuzu 6HK1 (2000s-Present)

Japanese precision engineering meets commercial truck reality.
The 6HK1 brings Isuzu’s legendary reliability to medium-duty trucking applications with 200-300 horsepower depending on configuration. This 7.8-liter turbodiesel features modern emissions controls and competitive fuel economy for its class. Parts availability has improved significantly in North American markets, though service network density still trails domestic manufacturers. The engine proves that Japanese commercial vehicle expertise extends beyond pickups and SUVs.
12. International MaxxForce DT (2007-2016)

Ambitious engineering that almost overcame its troubled predecessor’s reputation.
The MaxxForce DT attempted to redeem International’s diesel reputation with modern electronics and emissions compliance. This 9.3-liter engine produced respectable power and initially showed promise in reliability testing. However, EGR system problems and aftertreatment issues continued plaguing International’s commercial customers. While improvements came with software updates, the MaxxForce name carried too much baggage from earlier failures to fully recover market confidence.
11. Scania DC16 (2000s-Present)
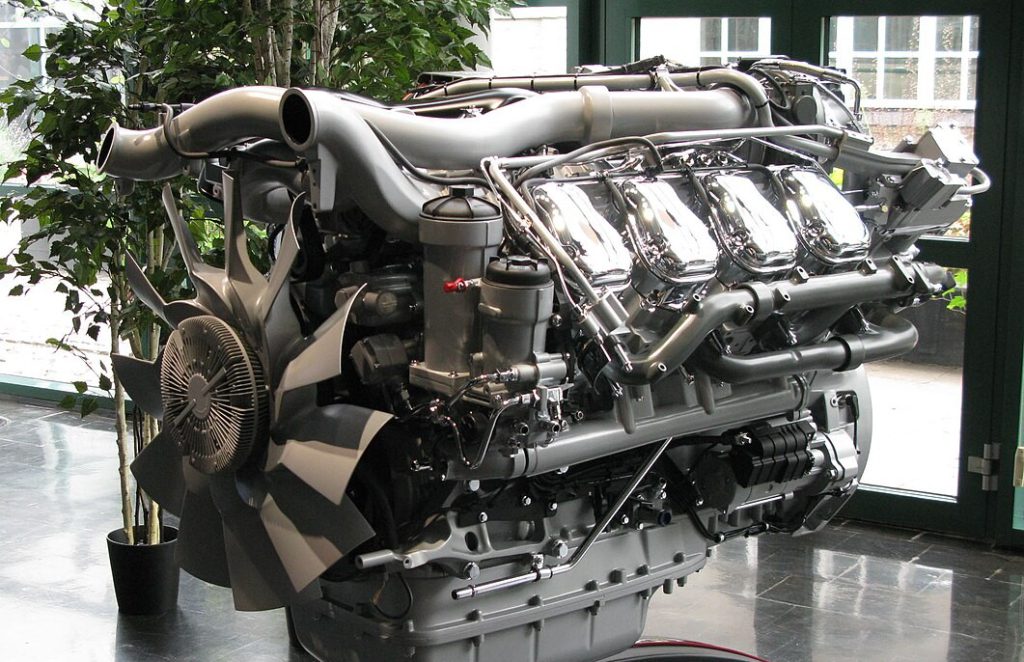
European sophistication meets global commercial vehicle demands.
The DC16 represents Scania’s flagship V8 diesel technology with outputs ranging from 520 to 730 horsepower in various configurations. This 16-liter powerplant combines impressive performance with surprisingly refined operation for such a large displacement engine. Premium pricing and limited North American availability restrict its market presence, but European operators appreciate the blend of power and efficiency. The DC16 proves that sophisticated engineering can coexist with commercial durability.
10. Caterpillar 3406E (1993-2003)

The yellow iron standard that defined an era of trucking.
Caterpillar 3406E dominated long-haul trucking through the 1990s with bulletproof mechanical reliability and impressive power output. This 14.6-liter inline-six produced 350-425 horsepower while maintaining the simplicity that fleet managers loved. Electronic controls added precision without sacrificing the rugged character that made Caterpillar engines legendary. Though fuel economy trailed newer designs, the 3406E’s reputation for running forever made it a favorite among owner-operators.
9. DAF MX-13 (2010s-Present)

European refinement meets American highway demands with impressive results.
The MX-13 brought PACCAR’s European engineering expertise to North American trucking markets with sophisticated emissions technology and competitive fuel economy. This 12.9-liter engine produces up to 510 horsepower while meeting strict environmental regulations without sacrificing reliability. Integration with Kenworth and Peterbilt chassis creates seamless powertrain combinations that drivers appreciate. The MX-13 proves that meeting modern emissions standards doesn’t require compromising performance or durability.
8. Mercedes OM471 (2010s-Present)

German precision engineering refined for global commercial applications.
The OM471 represents Mercedes-Benz’s latest generation diesel technology with outputs ranging from 428 to 625 horsepower across various configurations. This 12.8-liter inline-six combines advanced combustion technology with sophisticated electronics for impressive efficiency and performance. European market success has been substantial, though North American availability remains limited to specialty applications. The OM471 showcases how traditional diesel engineering can evolve to meet stringent modern requirements.
7. Volvo D13 (2000s-Present)

Scandinavian engineering evolution that prioritizes efficiency and driver experience.
The D13 builds upon Volvo’s truck engine heritage with advanced technology and impressive fuel economy for long-haul applications. This 12.8-liter engine produces up to 500 horsepower while integrating seamlessly with Volvo’s automated transmission systems. Sophisticated electronics optimize performance across varying load and terrain conditions. Driver-focused features and excellent support network make the D13 a strong choice for fleet operators prioritizing total cost of ownership over initial purchase price.
6. Detroit Diesel DD15 (2007-Present)

Modern two-valve technology that proves simplicity still has advantages.
The DD15 resurrects Detroit Diesel’s reputation with proven reliability and competitive performance in long-haul applications. This 14.8-liter inline-six produces up to 560 horsepower while maintaining the straightforward design philosophy that made earlier Detroit engines legendary. Two-valve cylinder heads reduce complexity compared to four-valve competitors without sacrificing power output. Strong aftermarket support and reasonable parts pricing make the DD15 attractive to cost-conscious operators.
5. International A26 (2017-Present)

European sophistication finally brings Navistar into the modern diesel era.
The A26 represents International’s partnership with MAN to deliver competitive technology after years of struggling with in-house designs. This 12.4-liter engine produces up to 475 horsepower while meeting emissions standards that previously challenged International’s engineering team. German engineering heritage provides the sophistication that International’s previous engines lacked. Early reliability reports suggest the A26 finally gives International a competitive powerplant for modern trucking applications.
4. Caterpillar C15 ACERT (2003-2009)

Advanced combustion technology that maintained Caterpillar’s reputation for durability.
The C15 ACERT represented Caterpillar’s response to stricter emissions regulations while preserving the reliability that made their engines legendary. This 15.8-liter inline-six produced up to 550 horsepower using advanced combustion and air handling technology instead of exhaust gas recirculation. Owner-operators appreciated maintaining traditional Cat engine characteristics while meeting environmental requirements. Though eventually replaced by newer designs, the C15 ACERT proved that innovative engineering could satisfy both regulators and customers.
3. Detroit Diesel DD16 (2014-Present)
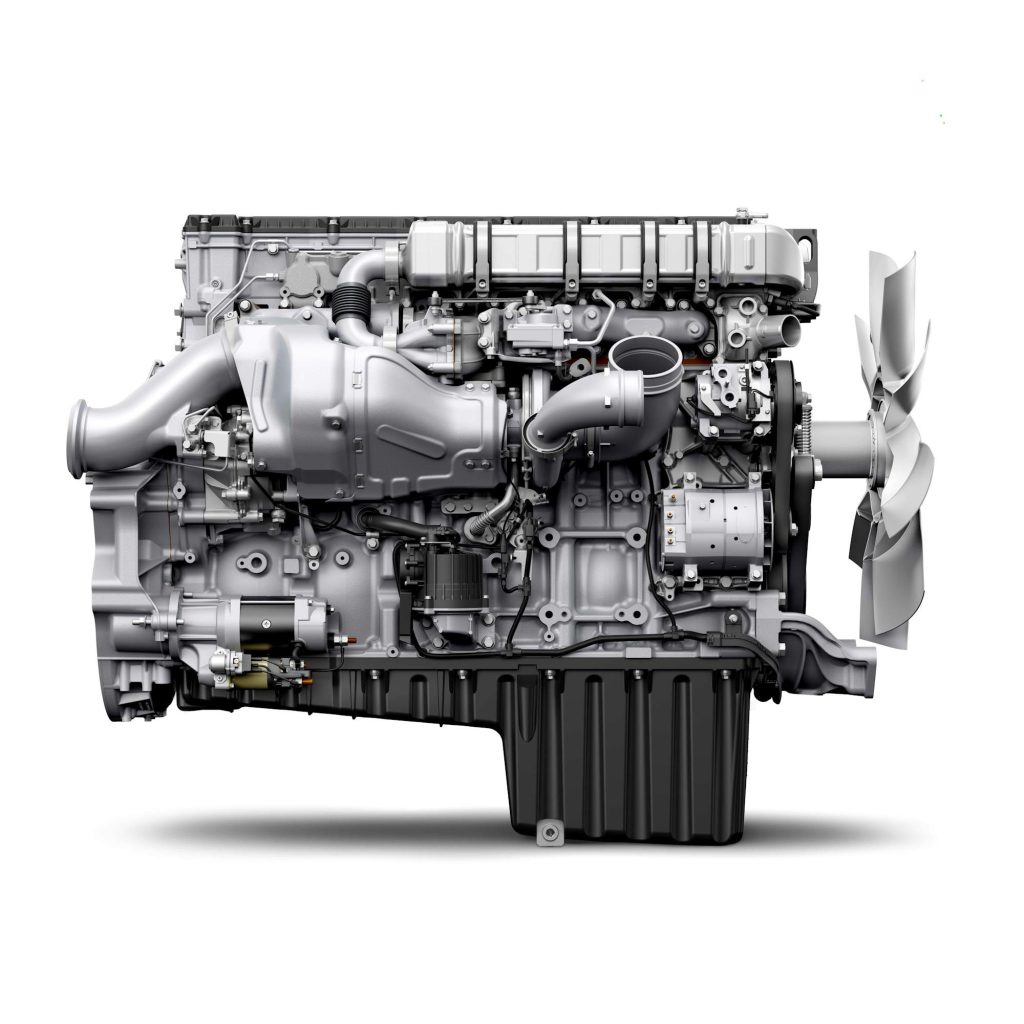
Maximum displacement meets modern technology for ultimate long-haul performance.
The DD16 delivers Detroit Diesel’s largest displacement in a package optimized for heavy-haul and demanding applications. This 15.6-liter inline-six produces up to 600 horsepower while maintaining fuel economy competitive with smaller engines through advanced technology. Sophisticated electronics optimize performance across varying loads and operating conditions. The DD16 proves that displacement and efficiency can coexist when engineering execution meets modern requirements.
2. Caterpillar C12 (1992-2003)

The goldilocks engine that balanced power, reliability, and efficiency perfectly.
The C12 hit the sweet spot between performance and practicality that made it legendary among truckers and fleet managers alike. This 12-liter inline-six produced 350-425 horsepower with mechanical reliability that seemed almost supernatural. Simple enough for roadside repairs yet sophisticated enough for modern highway demands, the C12 earned devotion from owner-operators who ran them past 1.5 million miles. Caterpillar discontinued it too soon, leaving a gap that competitors struggled to fill with equivalent simplicity and durability.
1. Toyota 1HD-T (1988-1995)
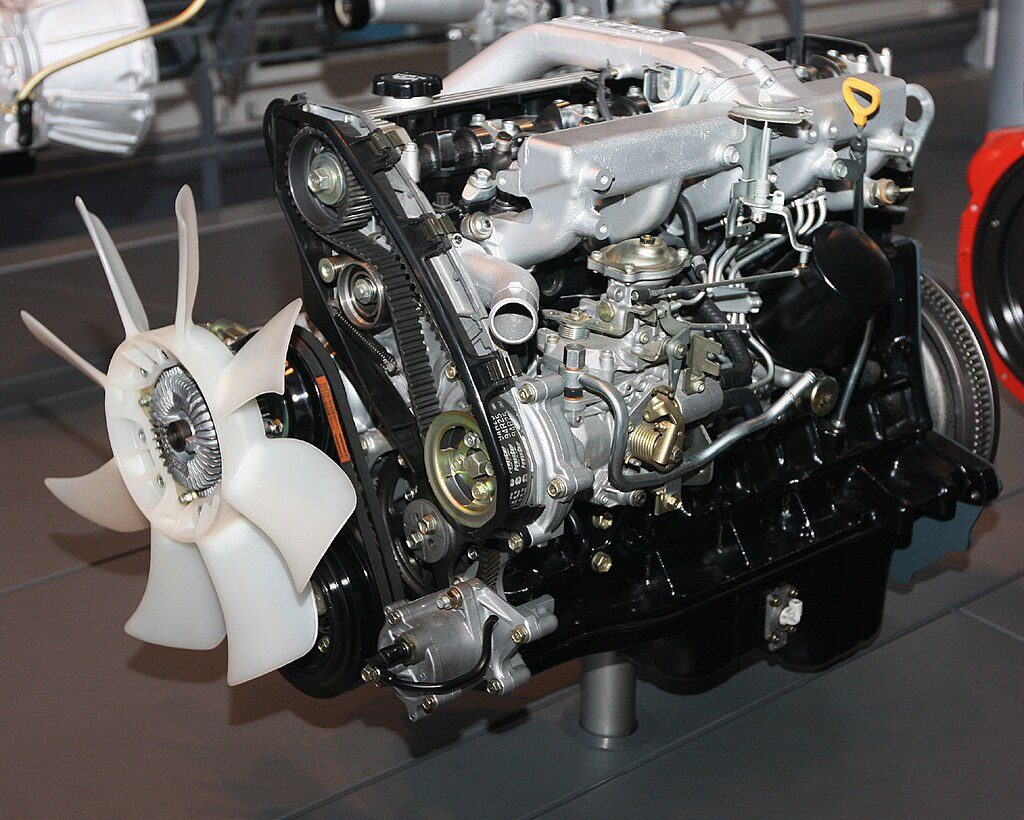
The ultimate expression of diesel engine philosophy: simple, reliable, and practically indestructible.
The 1HD-T represents everything a workhorse engine should be, even if its 4.2-liter displacement and 165 horsepower seem modest by modern standards. This turbocharged straight-six powered Land Cruiser HDJ80 and HDJ81 models across global markets with cast iron construction and mechanical fuel injection that laughed at poor fuel quality and harsh conditions. Anyone who’s traveled remote regions knows the drill—when other engines fail, Toyota diesels keep running.
The 1HD-T earned its reputation through decades of faithful service in African bush, Australian outback, and Middle Eastern desert conditions where complexity equals catastrophe. Simple maintenance requirements, bulletproof reliability, and Toyota’s legendary parts support network made this engine the gold standard for utility and overland applications. While modern engines offer more power and sophistication, none match the 1HD-T’s combination of simplicity and durability that defined Toyota’s diesel legacy.