The global tech landscape is buzzing with innovations that sound like science fiction but are already reshaping how we work, live, and play. From robots that think like ant colonies to AI that can predict your next craving, these breakthrough technologies are moving from lab experiments to real-world applications faster than a TikTok trend goes viral. While some promise to revolutionize entire industries, others are quietly making everyday life a little more magical. Here are the 15 amazing technologies that are about to flip the script on everything we thought we knew about the future.
15. Swarm Robotics and Collective AI

Swarm robotics takes inspiration from nature’s best collaborators—ants, bees, and birds—to create large groups of simple robots that coordinate without a central controller. Harvard’s Wyss Institute has already demonstrated programmable robot swarms with over 1,000 units working as one. The global swarm robotics market is projected to explode from $1.11 billion in 2025 to nearly $14.7 billion by 2034, growing at over 30% annually. These mechanical teams are being piloted for disaster response, where they can search dangerous zones too risky for humans, and in agriculture for crop monitoring and sustainable farming practices.
14. Brain-Computer Interfaces

Brain-computer interfaces are bridging the gap between mind and machine with neural implants that translate thoughts into digital actions. Companies like Neuralink and Synchron are developing systems that help paralyzed patients control computers, prosthetics, and wheelchairs using only their thoughts. Early trials show patients typing at speeds approaching normal conversation rates. Beyond medical applications, researchers are exploring how these interfaces might eventually allow direct brain-to-brain communication or instant access to digital information.
13. Quantum Computing
Quantum computers harness the weird physics of subatomic particles to solve problems that would take classical computers millennia. IBM, Google, and startups like IonQ are racing to build stable quantum systems that could revolutionize drug discovery, financial modeling, and cryptography. Google’s quantum computer recently solved a complex problem in 200 seconds that would take the world’s fastest supercomputer 10,000 years. While still experimental, quantum computing promises to crack previously unsolvable challenges in climate modeling and materials science.
12. Synthetic Biology

Synthetic biology lets scientists design and build new biological systems from scratch, creating everything from bacteria that eat plastic to yeast that produces spider silk. Companies like Ginkgo Bioworks are programming microorganisms to manufacture medicines, materials, and even food ingredients. Researchers have successfully engineered algae to produce jet fuel and bacteria to create sustainable leather alternatives. This field could solve major environmental challenges while creating entirely new categories of renewable materials.
11. Extended Reality (XR)

Extended Reality combines virtual reality, augmented reality, and mixed reality into seamless experiences that blend digital and physical worlds. Apple’s Vision Pro and Meta’s Quest headsets are pushing XR beyond gaming into practical applications like remote surgery training, architectural visualization, and virtual collaboration. Surgeons are using AR to overlay patient data during operations, while retailers let customers virtually try on clothes or furniture before buying. As hardware becomes lighter and more affordable, XR is positioned to become the next major computing platform.
10. Edge AI

Edge AI brings machine learning directly to smartphones, cameras, and IoT devices, eliminating the need for cloud connectivity. This means facial recognition works instantly on your phone, smart cameras can detect intruders without internet, and autonomous vehicles can make split-second decisions locally. Companies like Qualcomm and NVIDIA are designing specialized chips that run AI models efficiently on battery-powered devices. Edge AI promises faster responses, better privacy, and continued functionality even when networks fail.
9. Digital Twins
Digital twins create real-time virtual replicas of physical objects, systems, or processes using sensors and AI. General Electric uses digital twins to monitor jet engines mid-flight, predicting maintenance needs before problems occur. Cities like Singapore are building digital twins to optimize traffic flow and energy usage. These virtual mirrors help companies test changes safely, predict equipment failures, and optimize performance without disrupting actual operations.
8. Precision Medicine
Precision medicine uses genetic information, lifestyle data, and environmental factors to customize treatments for individual patients. Companies like 23andMe and Foundation Medicine analyze genetic markers to predict disease risks and drug responses. Oncologists now routinely sequence tumor DNA to select targeted cancer therapies. Pharmacogenomics tests help doctors prescribe medications based on how patients’ genes affect drug metabolism, reducing adverse reactions and improving effectiveness.
7. Autonomous Vehicles
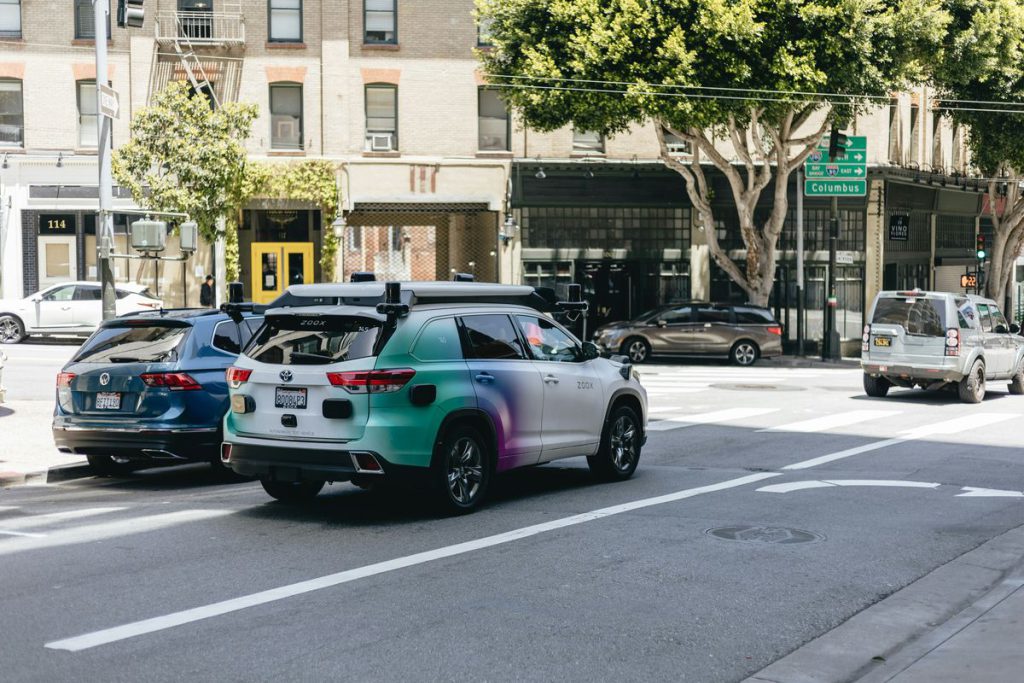

Autonomous vehicles combine sensors, cameras, and AI to navigate without human input. Waymo operates fully autonomous taxi services in Phoenix and San Francisco, while Tesla continues expanding its Full Self-Driving capabilities. These vehicles use real-time data processing to make thousands of driving decisions per second, potentially reducing traffic accidents caused by human error. Beyond personal transportation, autonomous trucks are being tested for long-haul freight delivery.
6. 3D Printing at Scale
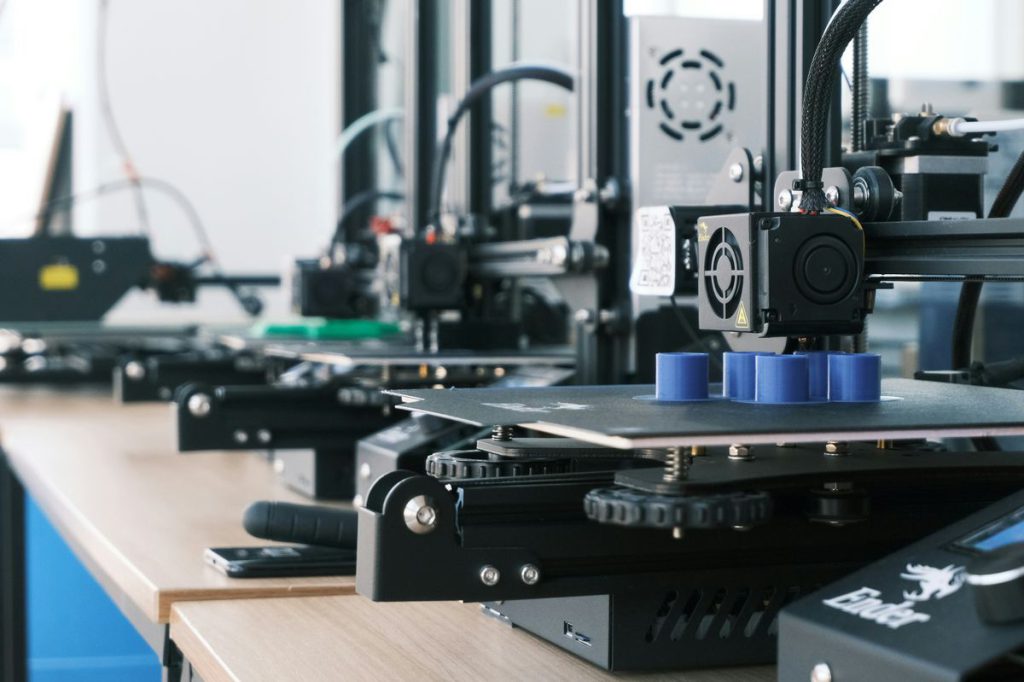

Advanced 3D printing is moving beyond prototypes to mass production of everything from car parts to human organs. Companies like Desktop Metal are 3D printing metal components for aerospace applications, while Organovo creates liver tissue for drug testing. Construction companies are 3D printing entire houses in under 24 hours. This technology enables on-demand manufacturing, reduces waste, and allows for complex designs impossible with traditional methods.
5. Renewable Energy Storage

Next-generation energy storage systems are solving renewable energy’s biggest challenge: what happens when the sun doesn’t shine and wind doesn’t blow. Tesla’s Megapack systems store excess solar and wind energy for later use, while companies like Form Energy are developing iron-air batteries that can store energy for days. These technologies are making renewable energy more reliable than fossil fuels, accelerating the transition to clean electricity grids.
4. Cellular Agriculture

Cellular agriculture grows real meat, dairy, and other animal products directly from cells without raising animals. Companies like Upside Foods and Eat Just have received regulatory approval to sell lab-grown chicken in select markets. This technology promises to reduce environmental impact, eliminate animal welfare concerns, and potentially make protein more affordable. Singapore became the first country to approve cultured meat for sale, with other nations following suit.
3. Advanced Nuclear Reactors

Small modular reactors (SMRs) and fusion power are reimagining nuclear energy with enhanced safety and efficiency. Companies like NuScale and Commonwealth Fusion Systems are developing reactors that automatically shut down safely and produce minimal waste. These advanced systems could provide clean, reliable baseload power to complement renewable sources. Some designs are small enough to power individual communities or industrial facilities.
2. Nanotechnology Applications
Nanotechnology manipulates materials at the molecular level to create products with extraordinary properties. Researchers have developed nanoparticles that deliver cancer drugs directly to tumors while sparing healthy cells. Self-cleaning surfaces use nanocoatings that break down dirt and bacteria when exposed to light. Carbon nanotubes create materials stronger than steel but lighter than aluminum, with applications in everything from spacecraft to sports equipment.
1. Biotechnology Convergence

The convergence of biotechnology with other fields is creating hybrid solutions that blur the lines between living and artificial systems. Researchers are developing biological computers that use DNA for data storage, potentially keeping information for thousands of years. Living materials that can self-repair and adapt to environmental changes are being tested for construction applications. This convergence promises to create technologies that are both more sustainable and more capable than purely artificial alternatives.