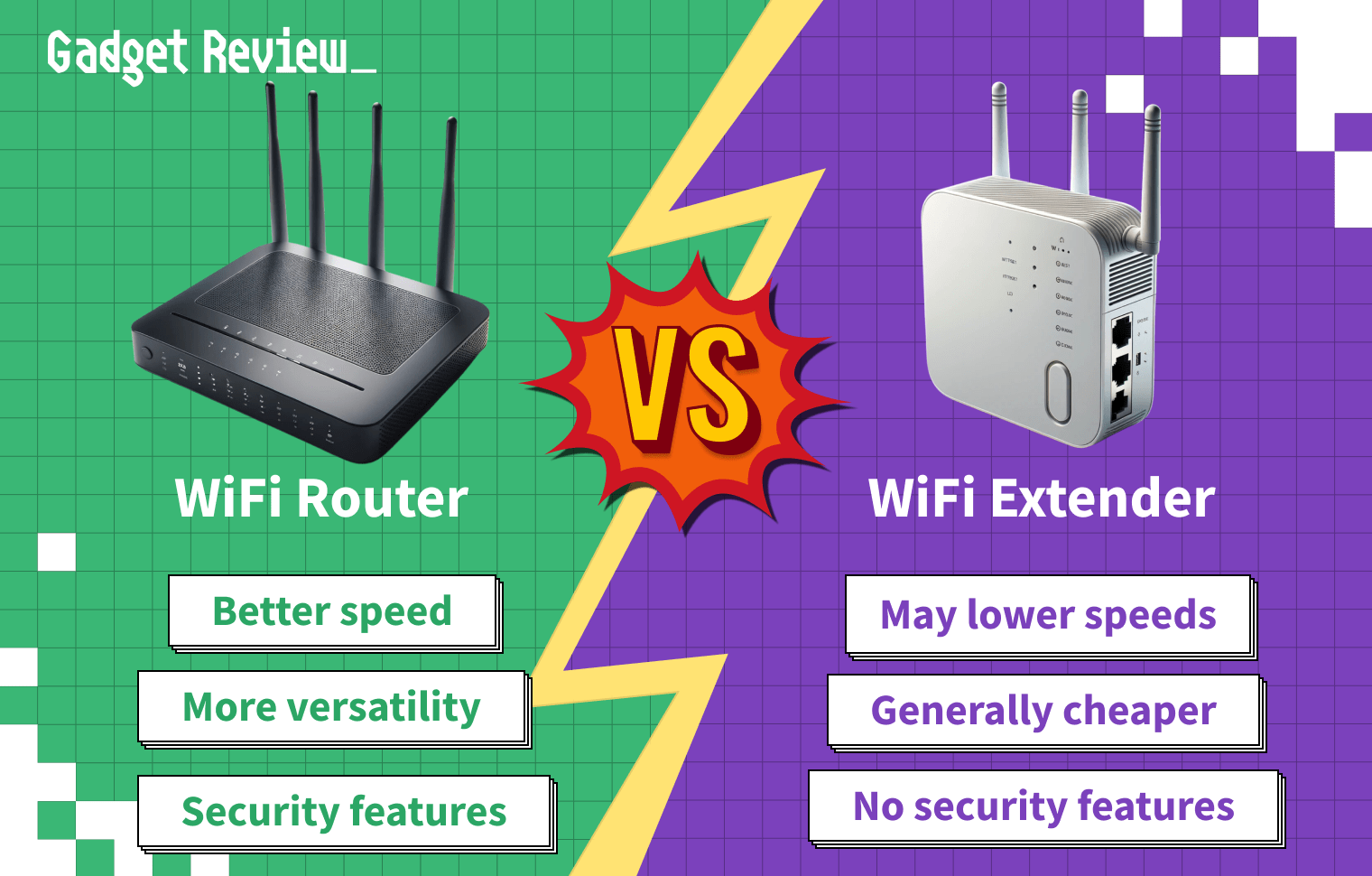
If you’re shopping for a way to start or expand a wireless network, you may wonder about the difference between a WiFi router vs. an extender. A WiFi router allows you to use the WiFi signal from your modem, while an extender increases the range of that WiFi signal.
Of course, the best router should have a large wireless range, but sometimes, you may need to upgrade your network equipment for the best results. So, if you want to eliminate wireless signal dead spots and get faster speeds, read on to see if a WiFi router or WiFi extender is right for you.
Key Takeaways_
- You cannot use a WiFi extender for the internet without first connecting it to a router.
- An extender takes the signal from your router and extends it over a wider area, cutting down on WiFi dead zones.
- A new WiFi router is the best choice if you want to improve your internet speeds.
Comparing WiFi Routers to Extenders
If you’re seeking improved WiFi coverage, it may seem obvious to pick up a wireless range extender, like a single-band or dual-band WiFi extender. However, it’s not that simple.
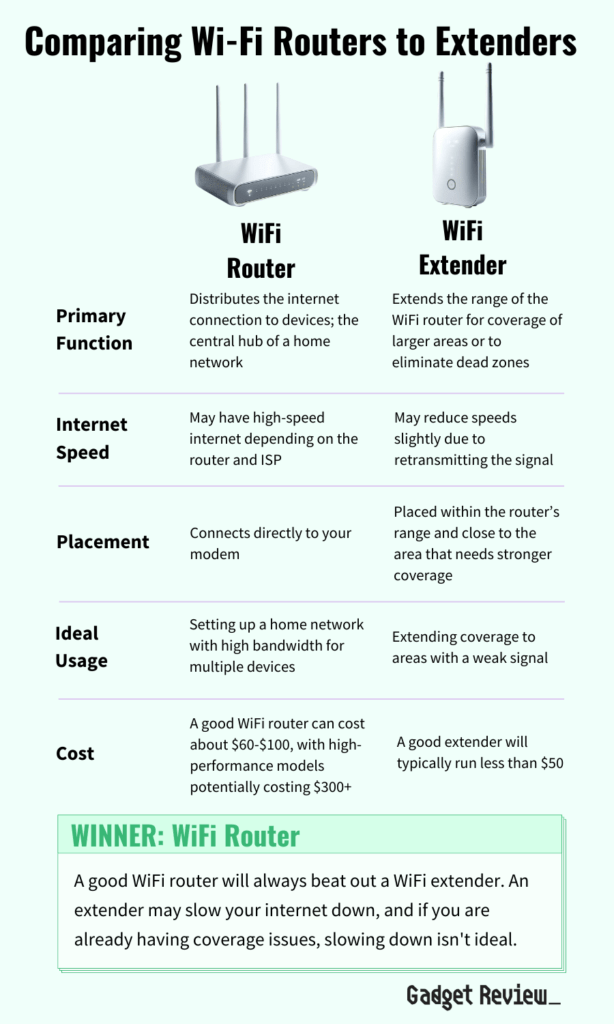
Comparing WiFi Routers to Extenders
| Feature | WiFi Router | WiFi Extender |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Distributes the internet connection to devices; the central hub of a home network | Extends the range of the WiFi router for coverage of larger areas or to eliminate dead zones |
| Internet Speed | May have high-speed internet depending on the router and ISP | May reduce speeds slightly due to retransmitting the signal |
| Placement | Connects directly to your modem | Placed within the router’s range and close to the area that needs stronger coverage |
| Ideal Usage | Setting up a home network with high bandwidth for multiple devices | Extending coverage to areas with a weak signal |
| Cost | A good WiFi router can cost about $60–$100, with high-performance models potentially costing $300+ | A good extender will typically run less than $50 |
A good WiFi router will always beat out a WiFi extender. An extender may slow your internet down, and if you are already having coverage issues, slowing down isn’t ideal.
For example, if you haven’t replaced your current router in a few years, your slow speeds are likely due to outdated hardware. This means you might have to pick up a new router, like an AC vs N wireless router.
Using a WiFi range extender will only compound the issue. In addition, WiFi extenders are used with a router, not in place of a router, so it’s best to have a great router before considering an extender.
insider tip
Make sure to update your router before investing in an extender. For example, new firmware might extend your router’s wireless range.
If you run a small business and want to expand your network coverage, consider a business router vs. a home router. Knowing the difference will make a big difference in your network’s performance.
WiFi Coverage
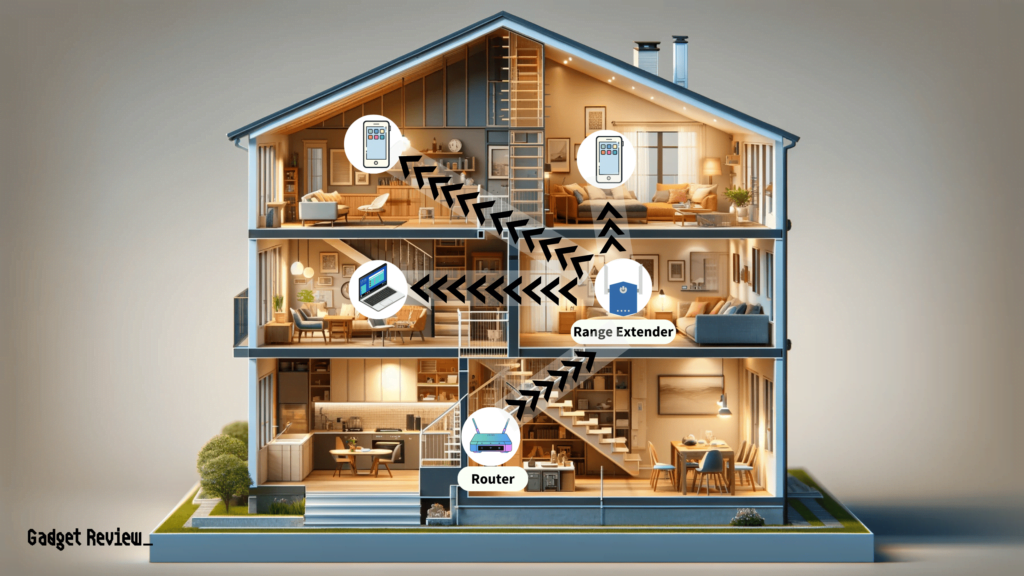
Modern wireless routers have improved WiFi coverage and multiple GHz bands for improved network prioritization and speed. That said, sometimes you need an extender’s help to reach certain rooms in your home.
This is because an extender will broadcast WiFi signals to a broader area. Still, you want to connect the extender to the router via Ethernet cable for best results.
warning
Unless you’ve updated all your other networking equipment, extenders may be a waste of money.
Internet Connection
A WiFi extender can expand your wireless connection but cannot work alone. To get an internet signal from an extender, you must connect it to a router, either with an ethernet connection or through your existing WiFi network signal.
STAT: As of 2021, 93% of adults in America at least occasionally use the internet. (source)
In short, an extender cannot connect you to the internet without a router.
Port Density
You don’t need to worry about wireless signal strength if you connect to the web with an Ethernet cable.
A high-end WiFi router will have multiple ways to connect to the internet, including several Ethernet ports for multiple wired connections.
While most extenders can support a couple of wired devices, it is not the ideal setup for an activity like online gaming.
Cost
If you already have a fantastic wireless router with the most up-to-date networking equipment, then investing in wireless extenders might be worth it.
That said, you may save some money by upgrading to a better WiFi router instead. For example, a newer router might have a better wireless range and allow for increased bandwidth.
When to Choose a Router
A router is the heart of your home network—it connects directly to your modem and manages all device communications. You should choose a router when:
- You’re setting up a new home or office network and need a central point for internet access.
- Your current router is outdated, slow, or lacking modern features like dual-band support, MU-MIMO, or WiFi 6/6E.
- You want full control over your network, including advanced features like parental controls, port forwarding, guest access, and device prioritization.
- You’re experiencing inconsistent internet throughout your home, and your current router’s range or performance just isn’t cutting it.
Bottom line: If you’re starting from scratch, upgrading, or need better management and speed, go with a new or better router.
When to Choose an Extender
A WiFi extender (also called a booster or repeater) takes the existing wireless signal from your router and rebroadcasts it to reach further. You should consider an extender when:
- You already have a solid router but experience dead zones in certain rooms or floors.
- Your home layout is large, multi-story, or has obstacles like thick walls that block signals.
- You need a quick, affordable fix for extending WiFi to a specific area—like a garage, backyard, or basement.
- You don’t want to replace your existing router but still want better coverage.
Keep in mind: Extenders can reduce speed slightly because they rebroadcast rather than directly route traffic. They’re great for casual use, but not ideal for gaming or 4K streaming in those extended zones.
Here is our helpful guide on How To Connect Two WiFi Extenders to improve your WiFi in your home or office. You may also want to read about Single Band Vs Dual Band WiFi Extenders to make sure you get the right option for your unique needs.
Mesh Systems vs Extenders – What’s the Difference? What Do You Need to Know?
Mesh WiFi systems and extenders both aim to eliminate dead zones—but how they work (and how well they work) are very different.
Mesh Systems:
- Work as a unified network: All nodes share the same network name (SSID), making handoffs between them seamless.
- Use smart routing algorithms: They direct traffic efficiently and choose the best path back to the modem.
- Ideal for large homes or demanding users: Gamers, remote workers, and smart home users benefit from the stability.
Extenders:
- Create a separate network (e.g., “YourWiFi_EXT”): You may have to manually switch between networks when moving around.
- Rely on your main router’s signal strength: If your router’s signal is weak in an area, the extender will struggle too.
- More affordable and easier to install, but not as seamless or reliable.
What You Need to Know:
- For simple fixes in small areas, an extender is fine.
- For whole-home coverage, especially in large or multi-level homes, go mesh.
- Mesh systems cost more, but the performance justifies it if you rely heavily on wireless connectivity.