When it comes to air conditioning, understanding BTU (British Thermal Unit) ratings is crucial for choosing the right unit for your space. BTU ratings, provided by standards such as ASHRAE and DOE, offer insights into the cooling capacity and efficiency of the top air conditioners. This article will explore the differences between ASHRAE and DOE BTU ratings, particularly focusing on portable air conditioners, to help consumers make informed decisions.
Key Takeaways_
- ASHRAE ratings were the first of their kind and can be applied to both window units and portable air conditioning systems.
- The Department of Energy (DOE) created a rating system using BTUs specific to portable ACs.
- Ratings for the DOE system incorporate infiltration from unconditioned air into your space.
Read on to learn what these abbreviations mean and how they measure the efficiency of your portable air conditioner. We’ve also listed other abbreviations at the bottom of this article that may be helpful in your search.
insider tip
DOE ratings provide a more accurate depiction of the AC’s efficiency.
What is BTU?
Before you can understand the differences between these two measurements, you need to understand what a BTU is.
BTU stands for British Thermal Unit and is a traditional measure used to quantify the cooling power of air conditioners.
It represents the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit. In the context of air conditioners, it measures the unit’s ability to remove heat from a space, thus indicating its cooling capacity.
To determine how many BTUs you need, you must consider the size of the space, insulation quality, and other factors affecting the room’s temperature
Understanding BTU is essential for selecting air conditioners that can efficiently control the temperature and humidity levels in your desired square feet of space.
ASHRAE vs. DOE: Comparison
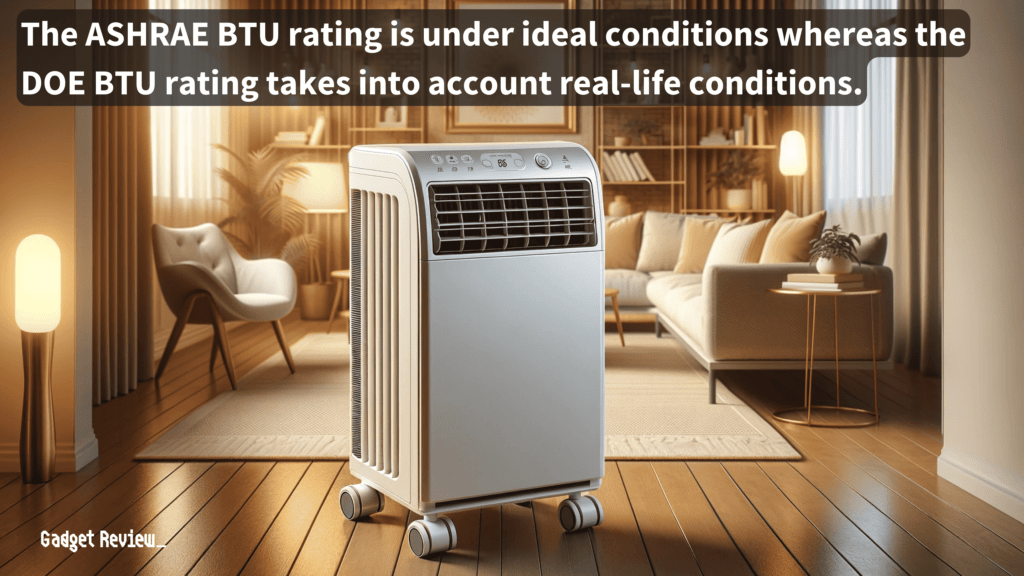
Comparing ASHRAE and DOE BTU ratings reveals significant differences in how each standard assesses the cooling capacity of portable air conditioners.
While ASHRAE ratings focus on the unit’s maximum potential in ideal conditions, DOE ratings offer a more realistic view by accounting for factors like heat generated by the unit’s operation and the efficiency of the exhaust system.
This comparison is crucial for consumers to understand as it affects the perceived efficiency and cooling power of portable AC units versus window units and other air conditioner types.
Understanding ASHRAE BTU Ratings
The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) developed a testing standard that measures the cooling capacity of air conditioners under ideal conditions.

ASHRAE BTU ratings are determined by evaluating the performance of portable units, window air conditioners, and other categories of air conditioners in controlled environments.
warning
ASHRAE ratings are not specific to portable air conditioners, so you may want to check the DOE rating as well.
This method ensures that the capacity ratings reflect the maximum cooling power an air conditioner can provide. However, these ideal testing conditions may not always represent the average performance of air conditioners in real-world applications.
Exploring DOE BTU Ratings
The Department of Energy (DOE) introduced a new testing method in 2017 for portable air conditioner units, known as the SACC (Seasonally Adjusted Cooling Capacity) BTU rating.

This approach considers factors such as the efficiency model, the impact of the exhaust hose, and the infiltration of warm air through openings, which are often overlooked by the ASHRAE testing standard.
The DOE’s method provides a more realistic measure of a portable air conditioner’s efficiency and performance, offering a weighted average of performance across various conditions, including different temperature and humidity levels.
Why the Difference Matters
The distinction between ASHRAE and DOE BTU ratings is more than just technical jargon; it has practical implications for consumers.
A higher ASHRAE rating might suggest exceptional cooling power, but the DOE rating often presents a more accurate picture of how the unit will perform in typical home conditions.
This difference can influence customer satisfaction, as it impacts the comfort level achieved by the portable air conditioner unit.
Understanding these ratings helps customers manage expectations and choose units that truly meet their cooling needs.
How to Choose the Right Air Conditioner
Selecting the right air conditioner involves more than just comparing BTU ratings. Consumers should consider the design and operation of the unit, including whether it’s a single-hose or dual-hose portable air conditioner, the combined energy efficiency ratio, and any additional efficiency ratings.
Understanding how tower AC works, which circulates air vertically through a tall, tower-like unit, can also be beneficial for those considering different types of air conditioning solutions.
STAT: A minimum efficiency of SEER 13 is recommended, though high-efficiency ACs may be cost-effective. (source)
It’s also important to assess the size of the space, the average temperature and humidity levels, and the specific applications of the air conditioner.
By taking these factors into account, along with the ASHRAE and DOE ratings, consumers can find an air conditioner that offers the best balance of cooling capacity and energy efficiency.
Additional Acronyms You’ll Find On AC Units
- The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) tracks and coordinates various standards and conformity within a wide range of systems, including those used to rate ACs.
- Before you start your portable air conditioning system search, consider the minimum efficiency rating value (MERV) for your designated air conditioner size. This rating represents the minimum requirement for the unit to be ENERGY STAR certified.
- The seasonal energy efficiency rating (SEER), similar to the seasonally adjusted cooling capacity (SACC,) states the average rating for the AC unit, taking into consideration the effects of the season and climate on the system’s efficiency. SEER is typically used on central AC units, so you may not encounter this abbreviation. However, SACC may be listed on each portable air conditioner model.
- You may also see references to the combined energy efficiency ratio (CEER) in the DOE BTU standard documentation. CEER combines the rating system of SEER with an additional efficiency rating when the system is on standby.
In the end, understanding the nuances between ASHRAE and DOE BTU ratings is essential for anyone looking to purchase an air conditioner.
These standards offer different perspectives on an air conditioner’s cooling capacity and efficiency, influencing how portable air conditioner manufacturers market their products.
By considering both ratings, along with other factors like space size and specific cooling needs, consumers can make more informed decisions, ensuring optimal comfort and efficiency from their chosen air conditioning units.